Table: Tree
+-------------+------+ | Column Name | Type | +-------------+------+ | id | int | | p_id | int | +-------------+------+ id is the column with unique values for this table. Each row of this table contains information about the id of a node and the id of its parent node in a tree. The given structure is always a valid tree.
Each node in the tree can be one of three types:
Write a solution to report the type of each node in the tree.
Return the result table in any order.
The result format is in the following example.
Example 1:
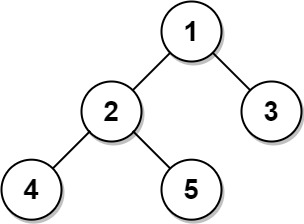
Input: Tree table: +----+------+ | id | p_id | +----+------+ | 1 | null | | 2 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | | 4 | 2 | | 5 | 2 | +----+------+ Output: +----+-------+ | id | type | +----+-------+ | 1 | Root | | 2 | Inner | | 3 | Leaf | | 4 | Leaf | | 5 | Leaf | +----+-------+ Explanation: Node 1 is the root node because its parent node is null and it has child nodes 2 and 3. Node 2 is an inner node because it has parent node 1 and child node 4 and 5. Nodes 3, 4, and 5 are leaf nodes because they have parent nodes and they do not have child nodes.
Example 2:

Input: Tree table: +----+------+ | id | p_id | +----+------+ | 1 | null | +----+------+ Output: +----+-------+ | id | type | +----+-------+ | 1 | Root | +----+-------+ Explanation: If there is only one node on the tree, you only need to output its root attributes.