You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes where each node in the tree has node.val coins. There are n coins in total throughout the whole tree.
In one move, we may choose two adjacent nodes and move one coin from one node to another. A move may be from parent to child, or from child to parent.
Return the minimum number of moves required to make every node have exactly one coin.
Example 1:
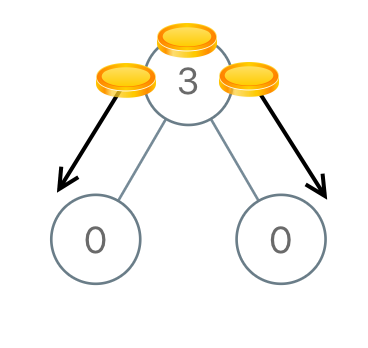
Input: root = [3,0,0] Output: 2 Explanation: From the root of the tree, we move one coin to its left child, and one coin to its right child.
Example 2:
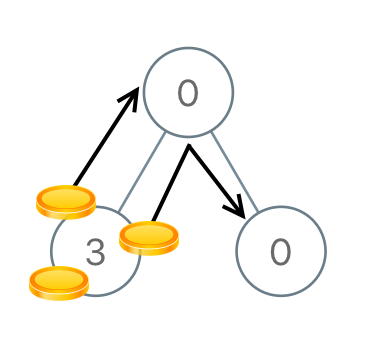
Input: root = [0,3,0] Output: 3 Explanation: From the left child of the root, we move two coins to the root [taking two moves]. Then, we move one coin from the root of the tree to the right child.
Constraints:
n.1 <= n <= 1000 <= Node.val <= nNode.val is n.