There exists an undirected and unrooted tree with n nodes indexed from 0 to n - 1. You are given an integer n and a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree. You are also given an array coins of size n where coins[i] can be either 0 or 1, where 1 indicates the presence of a coin in the vertex i.
Initially, you choose to start at any vertex in the tree. Then, you can perform the following operations any number of times:
2 from the current vertex, orFind the minimum number of edges you need to go through to collect all the coins and go back to the initial vertex.
Note that if you pass an edge several times, you need to count it into the answer several times.
Example 1:
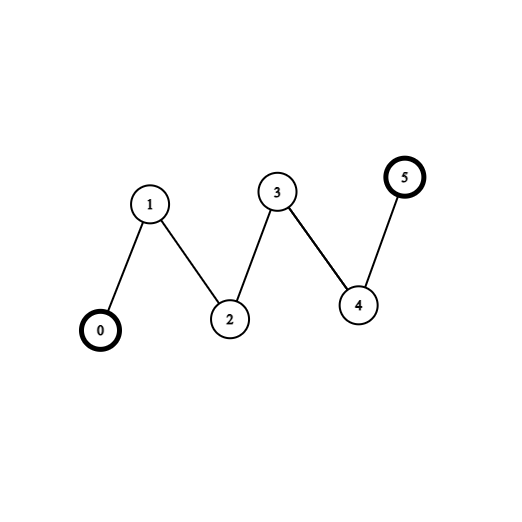
Input: coins = [1,0,0,0,0,1], edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5]] Output: 2 Explanation: Start at vertex 2, collect the coin at vertex 0, move to vertex 3, collect the coin at vertex 5 then move back to vertex 2.
Example 2:
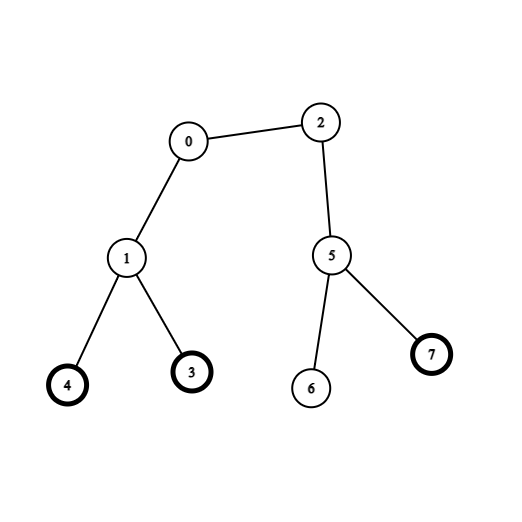
Input: coins = [0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1], edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[5,6],[5,7]] Output: 2 Explanation: Start at vertex 0, collect the coins at vertices 4 and 3, move to vertex 2, collect the coin at vertex 7, then move back to vertex 0.
Constraints:
n == coins.length1 <= n <= 3 * 1040 <= coins[i] <= 1edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != biedges represents a valid tree.