There is an m x n matrix that is initialized to all 0's. There is also a 2D array indices where each indices[i] = [ri, ci] represents a 0-indexed location to perform some increment operations on the matrix.
For each location indices[i], do both of the following:
ri.ci.Given m, n, and indices, return the number of odd-valued cells in the matrix after applying the increment to all locations in indices.
Example 1:
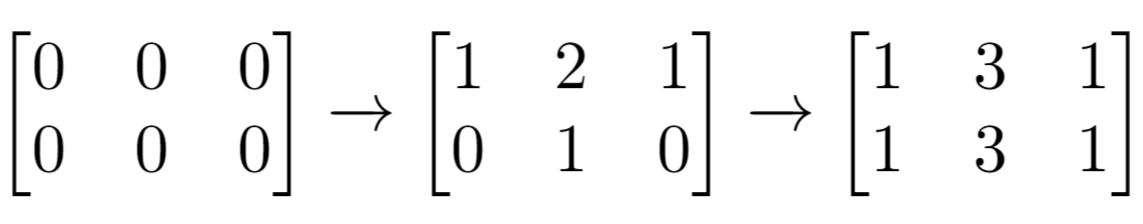
Input: m = 2, n = 3, indices = [[0,1],[1,1]] Output: 6 Explanation: Initial matrix = [[0,0,0],[0,0,0]]. After applying first increment it becomes [[1,2,1],[0,1,0]]. The final matrix is [[1,3,1],[1,3,1]], which contains 6 odd numbers.
Example 2:
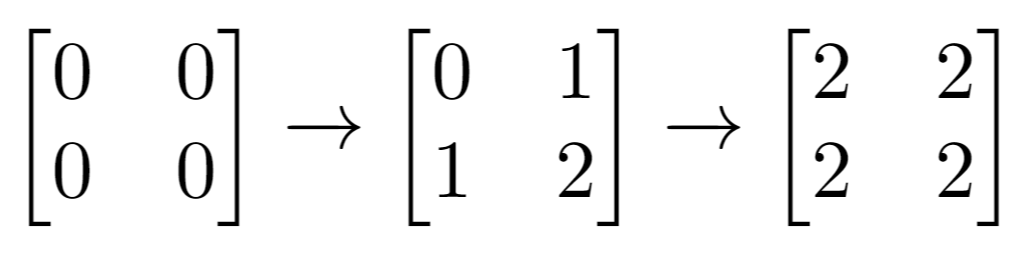
Input: m = 2, n = 2, indices = [[1,1],[0,0]] Output: 0 Explanation: Final matrix = [[2,2],[2,2]]. There are no odd numbers in the final matrix.
Constraints:
1 <= m, n <= 501 <= indices.length <= 1000 <= ri < m0 <= ci < n
Follow up: Could you solve this in O(n + m + indices.length) time with only O(n + m) extra space?