
你会得到一个字符串 s (索引从 0 开始),你必须对它执行 k 个替换操作。替换操作以三个长度均为 k 的并行数组给出:indices, sources, targets。
要完成第 i 个替换操作:
sources[i] 是否出现在 原字符串 s 的索引 indices[i] 处。targets[i] 替换 该子字符串。例如,如果 s = "abcd" , indices[i] = 0 , sources[i] = "ab", targets[i] = "eee" ,那么替换的结果将是 "eeecd" 。
所有替换操作必须 同时 发生,这意味着替换操作不应该影响彼此的索引。测试用例保证元素间不会重叠 。
s = "abc" , indices = [0,1] , sources = ["ab","bc"] 的测试用例将不会生成,因为 "ab" 和 "bc" 替换重叠。在对 s 执行所有替换操作后返回 结果字符串 。
子字符串 是字符串中连续的字符序列。
示例 1:

输入:s = "abcd", indices = [0,2], sources = ["a","cd"], targets = ["eee","ffff"] 输出:"eeebffff" 解释: "a" 从 s 中的索引 0 开始,所以它被替换为 "eee"。 "cd" 从 s 中的索引 2 开始,所以它被替换为 "ffff"。
示例 2: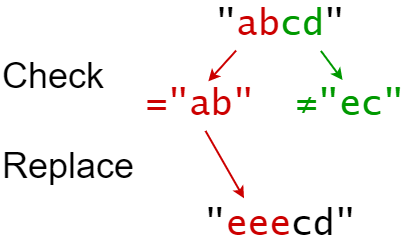
输入:s = "abcd", indices = [0,2], sources = ["ab","ec"], targets = ["eee","ffff"] 输出:"eeecd" 解释: "ab" 从 s 中的索引 0 开始,所以它被替换为 "eee"。 "ec" 没有从原始的 S 中的索引 2 开始,所以它没有被替换。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1000k == indices.length == sources.length == targets.length1 <= k <= 1000 <= indices[i] < s.length1 <= sources[i].length, targets[i].length <= 50s 仅由小写英文字母组成sources[i] 和 targets[i] 仅由小写英文字母组成