Given the root of a perfect binary tree, reverse the node values at each odd level of the tree.
[2,1,3,4,7,11,29,18], then it should become [18,29,11,7,4,3,1,2].Return the root of the reversed tree.
A binary tree is perfect if all parent nodes have two children and all leaves are on the same level.
The level of a node is the number of edges along the path between it and the root node.
Example 1:
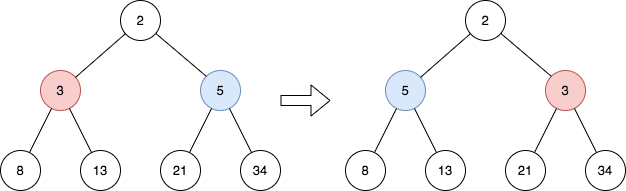
Input: root = [2,3,5,8,13,21,34] Output: [2,5,3,8,13,21,34] Explanation: The tree has only one odd level. The nodes at level 1 are 3, 5 respectively, which are reversed and become 5, 3.
Example 2:
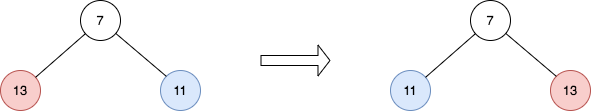
Input: root = [7,13,11] Output: [7,11,13] Explanation: The nodes at level 1 are 13, 11, which are reversed and become 11, 13.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,2,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2] Output: [0,2,1,0,0,0,0,2,2,2,2,1,1,1,1] Explanation: The odd levels have non-zero values. The nodes at level 1 were 1, 2, and are 2, 1 after the reversal. The nodes at level 3 were 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, and are 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1 after the reversal.
Constraints:
[1, 214].0 <= Node.val <= 105root is a perfect binary tree.