You are given an integer n representing the number of nodes in a perfect binary tree consisting of nodes numbered from 1 to n. The root of the tree is node 1 and each node i in the tree has two children where the left child is the node 2 * i and the right child is 2 * i + 1.
Each node in the tree also has a cost represented by a given 0-indexed integer array cost of size n where cost[i] is the cost of node i + 1. You are allowed to increment the cost of any node by 1 any number of times.
Return the minimum number of increments you need to make the cost of paths from the root to each leaf node equal.
Note:
Example 1:
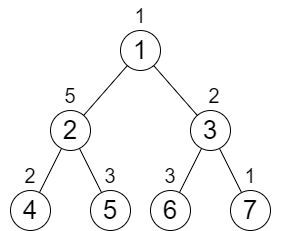
Input: n = 7, cost = [1,5,2,2,3,3,1] Output: 6 Explanation: We can do the following increments: - Increase the cost of node 4 one time. - Increase the cost of node 3 three times. - Increase the cost of node 7 two times. Each path from the root to a leaf will have a total cost of 9. The total increments we did is 1 + 3 + 2 = 6. It can be shown that this is the minimum answer we can achieve.
Example 2:
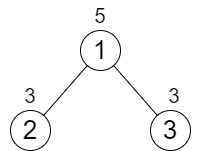
Input: n = 3, cost = [5,3,3] Output: 0 Explanation: The two paths already have equal total costs, so no increments are needed.
Constraints:
3 <= n <= 105n + 1 is a power of 2cost.length == n1 <= cost[i] <= 104