You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums whose length is a power of 2.
Apply the following algorithm on nums:
n be the length of nums. If n == 1, end the process. Otherwise, create a new 0-indexed integer array newNums of length n / 2.i where 0 <= i < n / 2, assign the value of newNums[i] as min(nums[2 * i], nums[2 * i + 1]).i where 0 <= i < n / 2, assign the value of newNums[i] as max(nums[2 * i], nums[2 * i + 1]).nums with newNums.Return the last number that remains in nums after applying the algorithm.
Example 1:
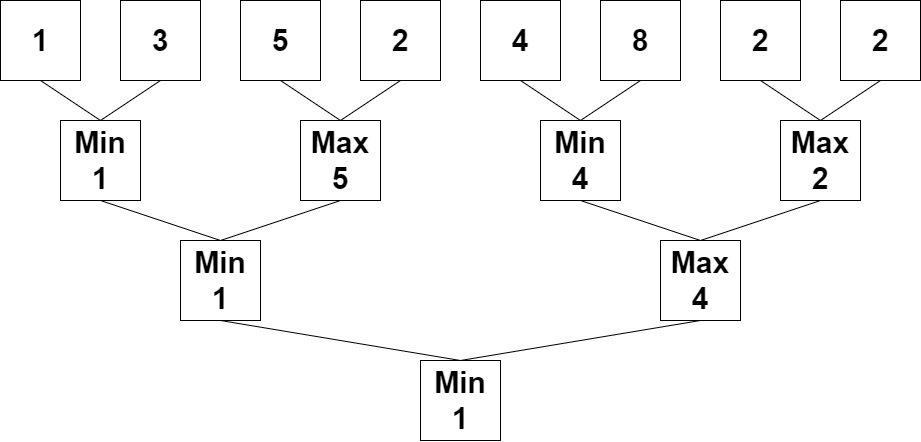
Input: nums = [1,3,5,2,4,8,2,2] Output: 1 Explanation: The following arrays are the results of applying the algorithm repeatedly. First: nums = [1,5,4,2] Second: nums = [1,4] Third: nums = [1] 1 is the last remaining number, so we return 1.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3] Output: 3 Explanation: 3 is already the last remaining number, so we return 3.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10241 <= nums[i] <= 109nums.length is a power of 2.