You are given a 0-indexed string s that you must perform k replacement operations on. The replacement operations are given as three 0-indexed parallel arrays, indices, sources, and targets, all of length k.
To complete the ith replacement operation:
sources[i] occurs at index indices[i] in the original string s.targets[i].For example, if s = "abcd", indices[i] = 0, sources[i] = "ab", and targets[i] = "eee", then the result of this replacement will be "eeecd".
All replacement operations must occur simultaneously, meaning the replacement operations should not affect the indexing of each other. The testcases will be generated such that the replacements will not overlap.
s = "abc", indices = [0, 1], and sources = ["ab","bc"] will not be generated because the "ab" and "bc" replacements overlap.Return the resulting string after performing all replacement operations on s.
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string.
Example 1:

Input: s = "abcd", indices = [0, 2], sources = ["a", "cd"], targets = ["eee", "ffff"] Output: "eeebffff" Explanation: "a" occurs at index 0 in s, so we replace it with "eee". "cd" occurs at index 2 in s, so we replace it with "ffff".
Example 2:
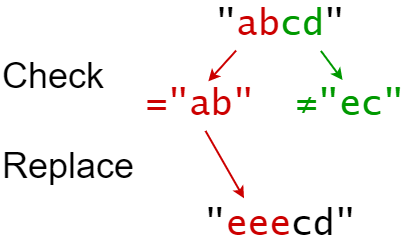
Input: s = "abcd", indices = [0, 2], sources = ["ab","ec"], targets = ["eee","ffff"] Output: "eeecd" Explanation: "ab" occurs at index 0 in s, so we replace it with "eee". "ec" does not occur at index 2 in s, so we do nothing.
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 1000k == indices.length == sources.length == targets.length1 <= k <= 1000 <= indexes[i] < s.length1 <= sources[i].length, targets[i].length <= 50s consists of only lowercase English letters.sources[i] and targets[i] consist of only lowercase English letters.