For a binary tree T, we can define a flip operation as follows: choose any node, and swap the left and right child subtrees.
A binary tree X is flip equivalent to a binary tree Y if and only if we can make X equal to Y after some number of flip operations.
Given the roots of two binary trees root1 and root2, return true if the two trees are flip equivalent or false otherwise.
Example 1:
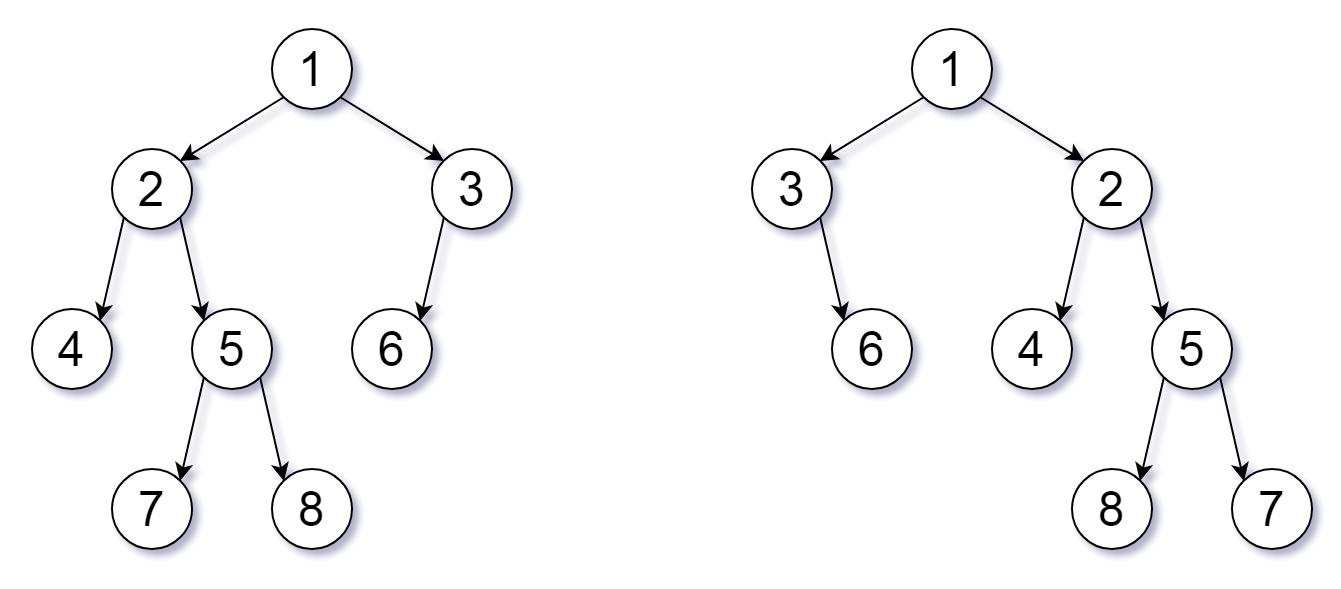
Input: root1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8], root2 = [1,3,2,null,6,4,5,null,null,null,null,8,7] Output: true Explanation: We flipped at nodes with values 1, 3, and 5.
Example 2:
Input: root1 = [], root2 = [] Output: true
Example 3:
Input: root1 = [], root2 = [1] Output: false
Constraints:
[0, 100].[0, 99].