Given the root of a binary tree, each node in the tree has a distinct value.
After deleting all nodes with a value in to_delete, we are left with a forest (a disjoint union of trees).
Return the roots of the trees in the remaining forest. You may return the result in any order.
Example 1:
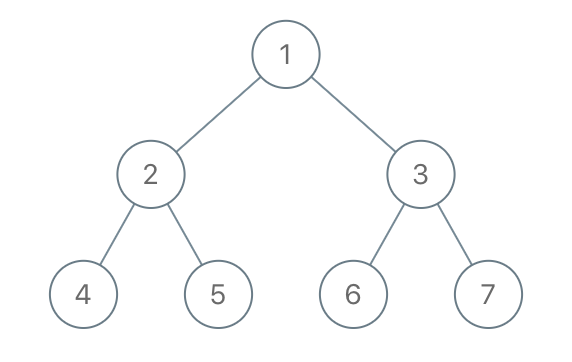
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], to_delete = [3,5] Output: [[1,2,null,4],[6],[7]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,4,null,3], to_delete = [3] Output: [[1,2,4]]
Constraints:
1000.1 and 1000.to_delete.length <= 1000to_delete contains distinct values between 1 and 1000.