Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [3,2,1]
Explanation:
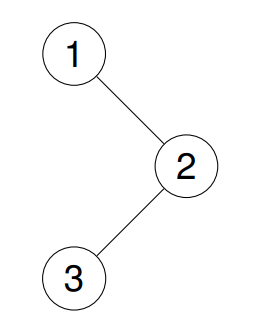
Given the root of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [3,2,1]
Explanation:

Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9]
Output: [4,6,7,5,2,9,8,3,1]
Explanation:
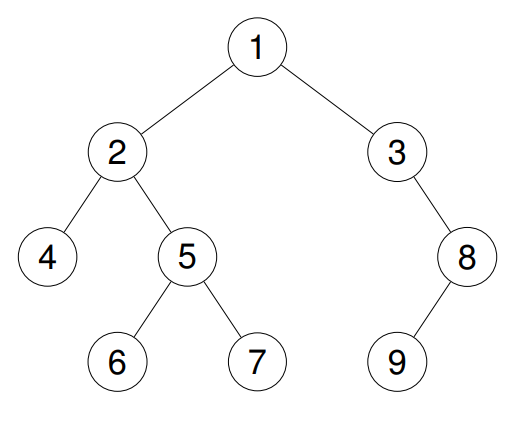
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 4:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
[0, 100].-100 <= Node.val <= 100Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?