Given an array arr of positive integers, consider all binary trees such that:
0 or 2 children;arr correspond to the values of each leaf in an in-order traversal of the tree.Among all possible binary trees considered, return the smallest possible sum of the values of each non-leaf node. It is guaranteed this sum fits into a 32-bit integer.
A node is a leaf if and only if it has zero children.
Example 1:
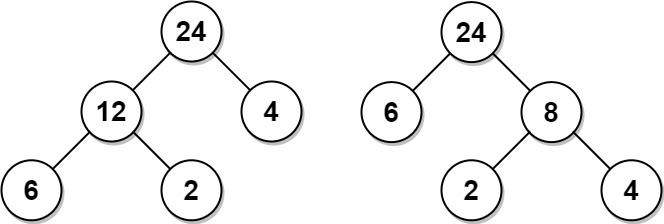
Input: arr = [6,2,4] Output: 32 Explanation: There are two possible trees shown. The first has a non-leaf node sum 36, and the second has non-leaf node sum 32.
Example 2:
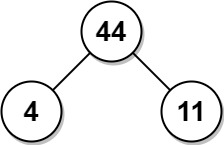
Input: arr = [4,11] Output: 44
Constraints:
2 <= arr.length <= 401 <= arr[i] <= 15