There is a binary tree rooted at 0 consisting of n nodes. The nodes are labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given a 0-indexed integer array parents representing the tree, where parents[i] is the parent of node i. Since node 0 is the root, parents[0] == -1.
Each node has a score. To find the score of a node, consider if the node and the edges connected to it were removed. The tree would become one or more non-empty subtrees. The size of a subtree is the number of the nodes in it. The score of the node is the product of the sizes of all those subtrees.
Return the number of nodes that have the highest score.
Example 1:
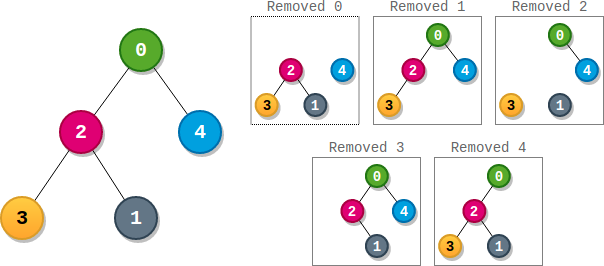
Input: parents = [-1,2,0,2,0] Output: 3 Explanation: - The score of node 0 is: 3 * 1 = 3 - The score of node 1 is: 4 = 4 - The score of node 2 is: 1 * 1 * 2 = 2 - The score of node 3 is: 4 = 4 - The score of node 4 is: 4 = 4 The highest score is 4, and three nodes (node 1, node 3, and node 4) have the highest score.
Example 2:
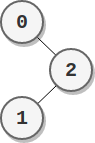
Input: parents = [-1,2,0] Output: 2 Explanation: - The score of node 0 is: 2 = 2 - The score of node 1 is: 2 = 2 - The score of node 2 is: 1 * 1 = 1 The highest score is 2, and two nodes (node 0 and node 1) have the highest score.
Constraints:
n == parents.length2 <= n <= 105parents[0] == -10 <= parents[i] <= n - 1 for i != 0parents represents a valid binary tree.