You are given an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
You are also given a 0-indexed integer array cost of length n, where cost[i] is the cost assigned to the ith node.
You need to place some coins on every node of the tree. The number of coins to be placed at node i can be calculated as:
i is less than 3, place 1 coin.3 distinct nodes in the subtree of node i. If this product is negative, place 0 coins.Return an array coin of size n such that coin[i] is the number of coins placed at node i.
Example 1:
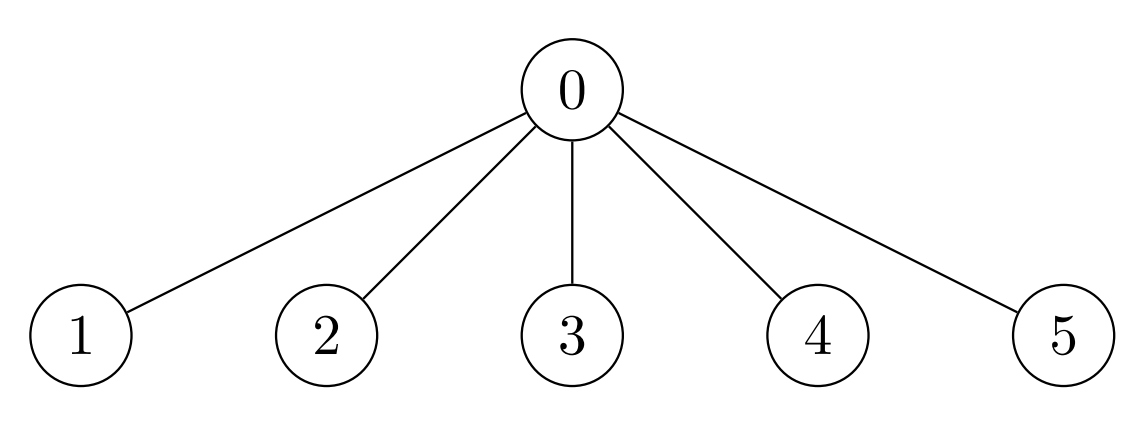
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5]], cost = [1,2,3,4,5,6] Output: [120,1,1,1,1,1] Explanation: For node 0 place 6 * 5 * 4 = 120 coins. All other nodes are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them.
Example 2:
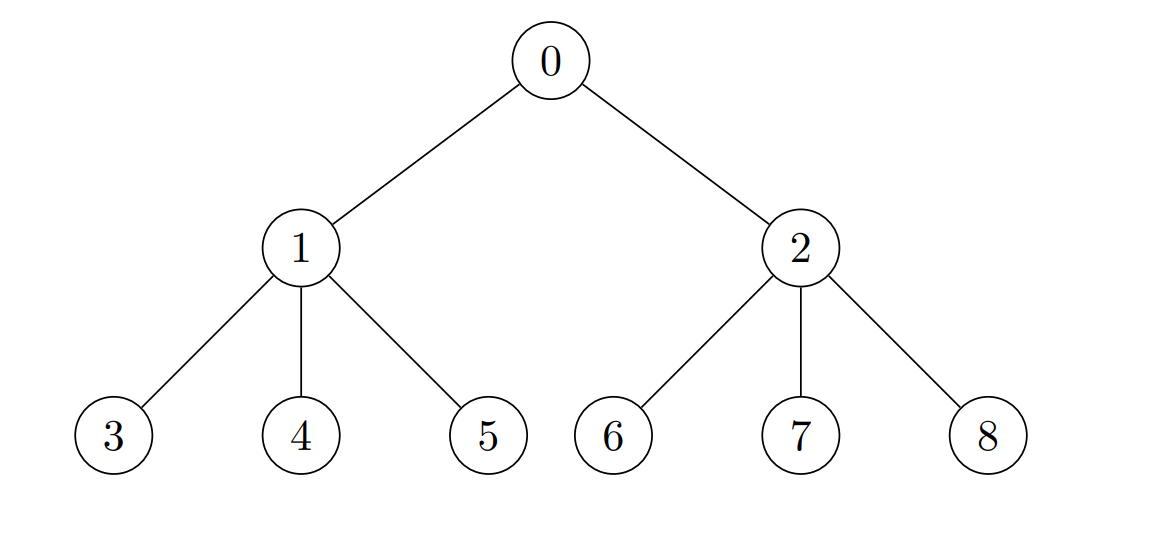
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[1,5],[2,6],[2,7],[2,8]], cost = [1,4,2,3,5,7,8,-4,2] Output: [280,140,32,1,1,1,1,1,1] Explanation: The coins placed on each node are: - Place 8 * 7 * 5 = 280 coins on node 0. - Place 7 * 5 * 4 = 140 coins on node 1. - Place 8 * 2 * 2 = 32 coins on node 2. - All other nodes are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them.
Example 3:
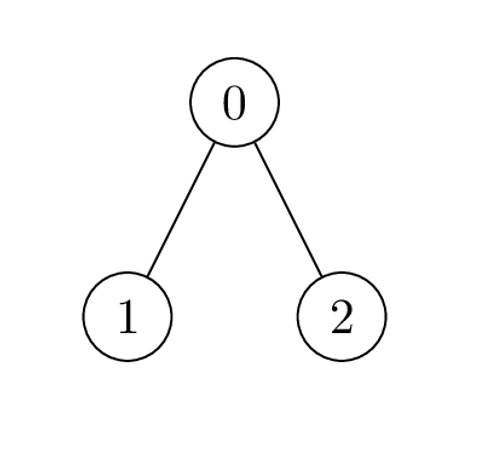
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2]], cost = [1,2,-2] Output: [0,1,1] Explanation: Node 1 and 2 are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them. For node 0 the only possible product of cost is 2 * 1 * -2 = -4. Hence place 0 coins on node 0.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 2 * 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < ncost.length == n1 <= |cost[i]| <= 104edges represents a valid tree.