Input: nums = [1,0,2]
Output: [0,1,2]
Explanation:
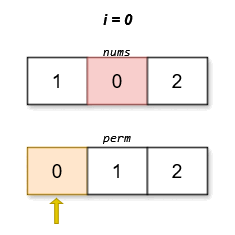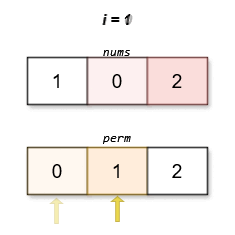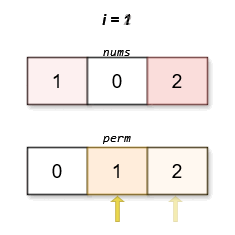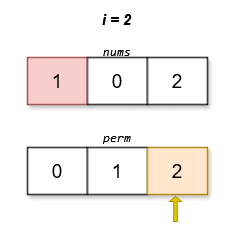
The lexicographically smallest permutation with minimum cost is [0,1,2]. The cost of this permutation is |0 - 0| + |1 - 2| + |2 - 1| = 2.
You are given an array nums which is a permutation of [0, 1, 2, ..., n - 1]. The score of any permutation of [0, 1, 2, ..., n - 1] named perm is defined as:
score(perm) = |perm[0] - nums[perm[1]]| + |perm[1] - nums[perm[2]]| + ... + |perm[n - 1] - nums[perm[0]]|
Return the permutation perm which has the minimum possible score. If multiple permutations exist with this score, return the one that is lexicographically smallest among them.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,0,2]
Output: [0,1,2]
Explanation:

The lexicographically smallest permutation with minimum cost is [0,1,2]. The cost of this permutation is |0 - 0| + |1 - 2| + |2 - 1| = 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,2,1]
Output: [0,2,1]
Explanation:
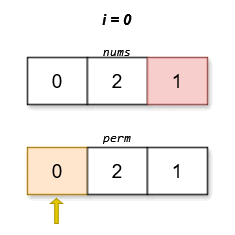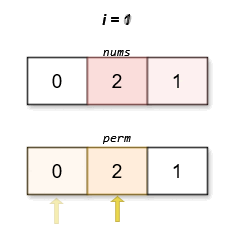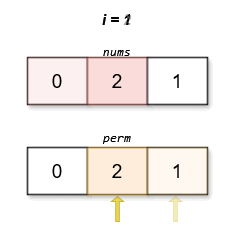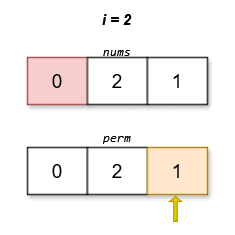
The lexicographically smallest permutation with minimum cost is [0,2,1]. The cost of this permutation is |0 - 1| + |2 - 2| + |1 - 0| = 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n == nums.length <= 14nums is a permutation of [0, 1, 2, ..., n - 1].