You are given a tree with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 in the form of a parent array parent where parent[i] is the parent of the ith node. The root of the tree is node 0, so parent[0] = -1 since it has no parent. You want to design a data structure that allows users to lock, unlock, and upgrade nodes in the tree.
The data structure should support the following functions:
Implement the LockingTree class:
LockingTree(int[] parent) initializes the data structure with the parent array.lock(int num, int user) returns true if it is possible for the user with id user to lock the node num, or false otherwise. If it is possible, the node num will become locked by the user with id user.unlock(int num, int user) returns true if it is possible for the user with id user to unlock the node num, or false otherwise. If it is possible, the node num will become unlocked.upgrade(int num, int user) returns true if it is possible for the user with id user to upgrade the node num, or false otherwise. If it is possible, the node num will be upgraded.
Example 1:
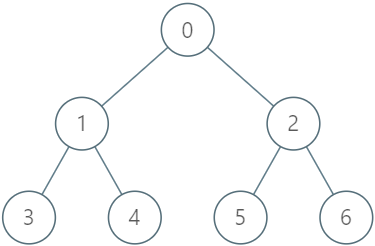
Input
["LockingTree", "lock", "unlock", "unlock", "lock", "upgrade", "lock"]
[[[-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]], [2, 2], [2, 3], [2, 2], [4, 5], [0, 1], [0, 1]]
Output
[null, true, false, true, true, true, false]
Explanation
LockingTree lockingTree = new LockingTree([-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]);
lockingTree.lock(2, 2); // return true because node 2 is unlocked.
// Node 2 will now be locked by user 2.
lockingTree.unlock(2, 3); // return false because user 3 cannot unlock a node locked by user 2.
lockingTree.unlock(2, 2); // return true because node 2 was previously locked by user 2.
// Node 2 will now be unlocked.
lockingTree.lock(4, 5); // return true because node 4 is unlocked.
// Node 4 will now be locked by user 5.
lockingTree.upgrade(0, 1); // return true because node 0 is unlocked and has at least one locked descendant (node 4).
// Node 0 will now be locked by user 1 and node 4 will now be unlocked.
lockingTree.lock(0, 1); // return false because node 0 is already locked.
Constraints:
n == parent.length2 <= n <= 20000 <= parent[i] <= n - 1 for i != 0parent[0] == -10 <= num <= n - 11 <= user <= 104parent represents a valid tree.2000 calls in total will be made to lock, unlock, and upgrade.