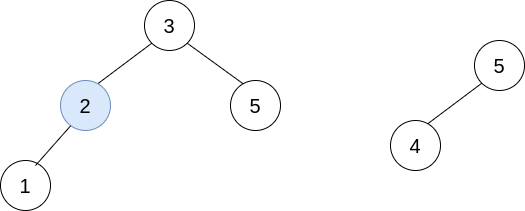
 In the second operation, pick i=0 and j=1, and merge trees[1] into trees[0].
Delete trees[1], so trees = [[3,2,5,1,null,4]].
In the second operation, pick i=0 and j=1, and merge trees[1] into trees[0].
Delete trees[1], so trees = [[3,2,5,1,null,4]].
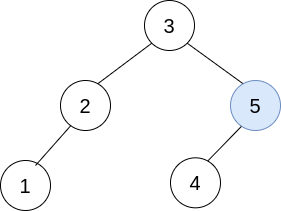 The resulting tree, shown above, is a valid BST, so return its root.
The resulting tree, shown above, is a valid BST, so return its root.You are given n BST (binary search tree) root nodes for n separate BSTs stored in an array trees (0-indexed). Each BST in trees has at most 3 nodes, and no two roots have the same value. In one operation, you can:
i and j such that the value stored at one of the leaves of trees[i] is equal to the root value of trees[j].trees[i] with trees[j].trees[j] from trees.Return the root of the resulting BST if it is possible to form a valid BST after performing n - 1 operations, or null if it is impossible to create a valid BST.
A BST (binary search tree) is a binary tree where each node satisfies the following property:
A leaf is a node that has no children.
Example 1:
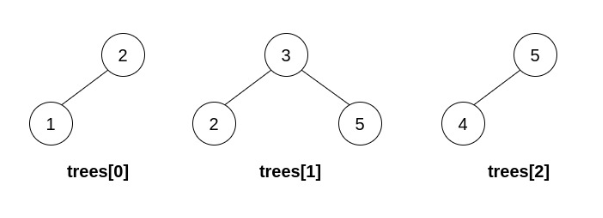
Input: trees = [[2,1],[3,2,5],[5,4]] Output: [3,2,5,1,null,4] Explanation: In the first operation, pick i=1 and j=0, and merge trees[0] into trees[1]. Delete trees[0], so trees = [[3,2,5,1],[5,4]].In the second operation, pick i=0 and j=1, and merge trees[1] into trees[0]. Delete trees[1], so trees = [[3,2,5,1,null,4]].
The resulting tree, shown above, is a valid BST, so return its root.
Example 2:
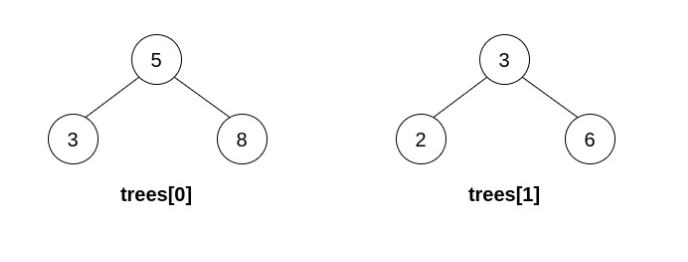
Input: trees = [[5,3,8],[3,2,6]] Output: [] Explanation: Pick i=0 and j=1 and merge trees[1] into trees[0]. Delete trees[1], so trees = [[5,3,8,2,6]].The resulting tree is shown above. This is the only valid operation that can be performed, but the resulting tree is not a valid BST, so return null.
Example 3:
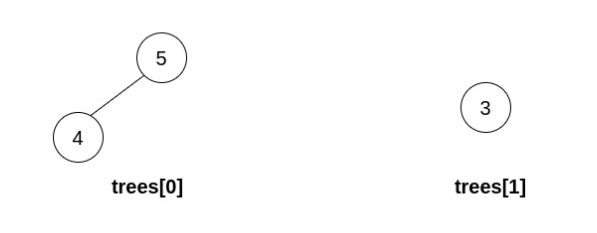
Input: trees = [[5,4],[3]] Output: [] Explanation: It is impossible to perform any operations.
Constraints:
n == trees.length1 <= n <= 5 * 104[1, 3].trees have the same value.1 <= TreeNode.val <= 5 * 104.