mirror of
https://gitee.com/coder-xiaomo/leetcode-problemset
synced 2025-11-08 21:35:48 +08:00
add leetcode problem-cn part2
This commit is contained in:
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个放有字母和数字的数组,找到最长的子数组,且包含的字母和数字的个数相同。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回该子数组,若存在多个最长子数组,返回左端点下标值最小的子数组。若不存在这样的数组,返回一个空数组。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>["A","1","B","C","D","2","3","4","E","5","F","G","6","7","H","I","J","K","L","M"]
|
||||
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>["A","1","B","C","D","2","3","4","E","5","F","G","6","7"]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>["A","A"]
|
||||
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>array.length <= 100000</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
30
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/0 和 1 个数相同的子数组 [A1NYOS].html
Normal file
30
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/0 和 1 个数相同的子数组 [A1NYOS].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个二进制数组 <code>nums</code> , 找到含有相同数量的 <code>0</code> 和 <code>1</code> 的最长连续子数组,并返回该子数组的长度。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> nums = [0,1]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 2
|
||||
<strong>说明:</strong> [0, 1] 是具有相同数量 0 和 1 的最长连续子数组。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> nums = [0,1,0]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 2
|
||||
<strong>说明:</strong> [0, 1] (或 [1, 0]) 是具有相同数量 0 和 1 的最长连续子数组。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>nums[i]</code> 不是 <code>0</code> 就是 <code>1</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 525 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/contiguous-array/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/contiguous-array/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
<p>一个长度为n-1的递增排序数组中的所有数字都是唯一的,并且每个数字都在范围0~n-1之内。在范围0~n-1内的n个数字中有且只有一个数字不在该数组中,请找出这个数字。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> [0,1,3]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 2
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,9]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 8</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>限制:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code>1 <= 数组长度 <= 10000</code></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
<p>输入一个整数 <code>n</code> ,求1~n这n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>例如,输入12,1~12这些整数中包含1 的数字有1、10、11和12,1一共出现了5次。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>n = 12
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>5
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>n = 13
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>6</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>限制:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n < 2^31</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意:本题与主站 233 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-digit-one/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-digit-one/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
<p>编写一个方法,计算从 0 到 n (含 n) 中数字 2 出现的次数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入: </strong>25
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>9
|
||||
<strong>解释: </strong>(2, 12, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25)(注意 22 应该算作两次)</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>提示:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>n <= 10^9</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
19
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/BiNode [binode-lcci].html
Normal file
19
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/BiNode [binode-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
<p>二叉树数据结构<code>TreeNode</code>可用来表示单向链表(其中<code>left</code>置空,<code>right</code>为下一个链表节点)。实现一个方法,把二叉搜索树转换为单向链表,要求依然符合二叉搜索树的性质,转换操作应是原址的,也就是在原始的二叉搜索树上直接修改。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回转换后的单向链表的头节点。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>注意:</strong>本题相对原题稍作改动</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> [4,2,5,1,3,null,6,0]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> [0,null,1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>节点数量不会超过 100000。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
<p>Excel 表中的一个单元格 <code>(r, c)</code> 会以字符串 <code>"<col><row>"</code> 的形式进行表示,其中:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code><col></code> 即单元格的列号 <code>c</code> 。用英文字母表中的 <strong>字母</strong> 标识。
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>例如,第 <code>1</code> 列用 <code>'A'</code> 表示,第 <code>2</code> 列用 <code>'B'</code> 表示,第 <code>3</code> 列用 <code>'C'</code> 表示,以此类推。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li><code><row></code> 即单元格的行号 <code>r</code> 。第 <code>r</code> 行就用 <strong>整数</strong> <code>r</code> 标识。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给你一个格式为 <code>"<col1><row1>:<col2><row2>"</code> 的字符串 <code>s</code> ,其中 <code><col1></code> 表示 <code>c1</code> 列,<code><row1></code> 表示 <code>r1</code> 行,<code><col2></code> 表示 <code>c2</code> 列,<code><row2></code> 表示 <code>r2</code> 行,并满足 <code>r1 <= r2</code> 且 <code>c1 <= c2</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>找出所有满足 <code>r1 <= x <= r2</code> 且 <code>c1 <= y <= c2</code> 的单元格,并以列表形式返回。单元格应该按前面描述的格式用 <strong>字符串</strong> 表示,并以 <strong>非递减</strong> 顺序排列(先按列排,再按行排)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2022/02/08/ex1drawio.png" style="width: 250px; height: 160px;" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>s = "K1:L2"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>["K1","K2","L1","L2"]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
上图显示了列表中应该出现的单元格。
|
||||
红色箭头指示单元格的出现顺序。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2022/02/09/exam2drawio.png" style="width: 500px; height: 50px;" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>s = "A1:F1"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>["A1","B1","C1","D1","E1","F1"]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
上图显示了列表中应该出现的单元格。
|
||||
红色箭头指示单元格的出现顺序。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>s.length == 5</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>'A' <= s[0] <= s[3] <= 'Z'</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>'1' <= s[1] <= s[4] <= '9'</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>s</code> 由大写英文字母、数字、和 <code>':'</code> 组成</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
<p>你正在设计一个动态数组。给你一个下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的整数数组 <code>nums</code> ,其中 <code>nums[i]</code> 是 <code>i</code> 时刻数组中的元素数目。除此以外,你还有一个整数 <code>k</code> ,表示你可以 <strong>调整</strong> 数组大小的 <strong>最多</strong> 次数(每次都可以调整成 <strong>任意</strong> 大小)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code>t</code> 时刻数组的大小 <code>size<sub>t</sub></code> 必须大于等于 <code>nums[t]</code> ,因为数组需要有足够的空间容纳所有元素。<code>t</code> 时刻 <strong>浪费的空间</strong> 为 <code>size<sub>t</sub> - nums[t]</code> ,<strong>总</strong> 浪费空间为满足 <code>0 <= t < nums.length</code> 的每一个时刻 <code>t</code> 浪费的空间 <strong>之和</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在调整数组大小不超过 <code>k</code> 次的前提下,请你返回 <strong>最小总浪费空间</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>注意:</strong>数组最开始时可以为 <strong>任意大小</strong> ,且 <strong>不计入</strong> 调整大小的操作次数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>nums = [10,20], k = 0
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>10
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>size = [20,20].
|
||||
我们可以让数组初始大小为 20 。
|
||||
总浪费空间为 (20 - 10) + (20 - 20) = 10 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>nums = [10,20,30], k = 1
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>10
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>size = [20,20,30].
|
||||
我们可以让数组初始大小为 20 ,然后时刻 2 调整大小为 30 。
|
||||
总浪费空间为 (20 - 10) + (20 - 20) + (30 - 30) = 10 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>nums = [10,20,15,30,20], k = 2
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>15
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>size = [10,20,20,30,30].
|
||||
我们可以让数组初始大小为 10 ,时刻 1 调整大小为 20 ,时刻 3 调整大小为 30 。
|
||||
总浪费空间为 (10 - 10) + (20 - 20) + (20 - 15) + (30 - 30) + (30 - 20) = 15 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums.length <= 200</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums[i] <= 10<sup>6</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= k <= nums.length - 1</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
21
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/LRU 缓存 [lru-cache-lcci].html
Normal file
21
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/LRU 缓存 [lru-cache-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
<p>设计和构建一个“最近最少使用”缓存,该缓存会删除最近最少使用的项目。缓存应该从键映射到值(允许你插入和检索特定键对应的值),并在初始化时指定最大容量。当缓存被填满时,它应该删除最近最少使用的项目。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 <code>get</code> 和 写入数据 <code>put</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>获取数据 <code>get(key)</code> - 如果密钥 (key) 存在于缓存中,则获取密钥的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。<br>
|
||||
写入数据 <code>put(key, value)</code> - 如果密钥不存在,则写入其数据值。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最近最少使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>LRUCache cache = new LRUCache( 2 /* 缓存容量 */ );
|
||||
|
||||
cache.put(1, 1);
|
||||
cache.put(2, 2);
|
||||
cache.get(1); // 返回 1
|
||||
cache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得密钥 2 作废
|
||||
cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
|
||||
cache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得密钥 1 作废
|
||||
cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
|
||||
cache.get(3); // 返回 3
|
||||
cache.get(4); // 返回 4
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
23
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/T9键盘 [t9-lcci].html
Normal file
23
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/T9键盘 [t9-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
<p>在老式手机上,用户通过数字键盘输入,手机将提供与这些数字相匹配的单词列表。每个数字映射到0至4个字母。给定一个数字序列,实现一个算法来返回匹配单词的列表。你会得到一张含有有效单词的列表。映射如下图所示:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img src="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/original_images/17_telephone_keypad.png" style="width: 200px;"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> num = "8733", words = ["tree", "used"]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> ["tree", "used"]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> num = "2", words = ["a", "b", "c", "d"]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> ["a", "b", "c"]</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>提示:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>num.length <= 1000</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>words.length <= 500</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>words[i].length == num.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>num</code>中不会出现 0, 1 这两个数字</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
25
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/URL化 [string-to-url-lcci].html
Normal file
25
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/URL化 [string-to-url-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
<p>URL化。编写一种方法,将字符串中的空格全部替换为<code>%20</code>。假定该字符串尾部有足够的空间存放新增字符,并且知道字符串的“真实”长度。(注:用<code>Java</code>实现的话,请使用字符数组实现,以便直接在数组上操作。)</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入</strong>:"Mr John Smith ", 13
|
||||
<strong>输出</strong>:"Mr%20John%20Smith"
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入</strong>:" ", 5
|
||||
<strong>输出</strong>:"%20%20%20%20%20"
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>字符串长度在 [0, 500000] 范围内。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
<p>一个 <strong>k 镜像数字</strong> 指的是一个在十进制和 k 进制下从前往后读和从后往前读都一样的 <strong>没有前导 0</strong> 的 <strong>正</strong> 整数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>比方说,<code>9</code> 是一个 2 镜像数字。<code>9</code> 在十进制下为 <code>9</code> ,二进制下为 <code>1001</code> ,两者从前往后读和从后往前读都一样。</li>
|
||||
<li>相反地,<code>4</code> 不是一个 2 镜像数字。<code>4</code> 在二进制下为 <code>100</code> ,从前往后和从后往前读不相同。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给你进制 <code>k</code> 和一个数字 <code>n</code> ,请你返回 k 镜像数字中 <strong>最小</strong> 的 <code>n</code> 个数 <strong>之和</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><b>示例 1:</b></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>k = 2, n = 5
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>25
|
||||
<strong>解释:
|
||||
</strong>最小的 5 个 2 镜像数字和它们的二进制表示如下:
|
||||
十进制 二进制
|
||||
1 1
|
||||
3 11
|
||||
5 101
|
||||
7 111
|
||||
9 1001
|
||||
它们的和为 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 = 25 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>k = 3, n = 7
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>499
|
||||
<strong>解释:
|
||||
</strong>7 个最小的 3 镜像数字和它们的三进制表示如下:
|
||||
十进制 三进制
|
||||
1 1
|
||||
2 2
|
||||
4 11
|
||||
8 22
|
||||
121 11111
|
||||
151 12121
|
||||
212 21212
|
||||
它们的和为 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + 121 + 151 + 212 = 499 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>k = 7, n = 17
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>20379000
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>17 个最小的 7 镜像数字分别为:
|
||||
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 121, 171, 242, 292, 16561, 65656, 2137312, 4602064, 6597956, 6958596
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>2 <= k <= 9</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n <= 30</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
<p>把n个骰子扔在地上,所有骰子朝上一面的点数之和为s。输入n,打印出s的所有可能的值出现的概率。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>你需要用一个浮点数数组返回答案,其中第 i 个元素代表这 n 个骰子所能掷出的点数集合中第 i 小的那个的概率。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> 1
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> [0.16667,0.16667,0.16667,0.16667,0.16667,0.16667]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> 2
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> [0.02778,0.05556,0.08333,0.11111,0.13889,0.16667,0.13889,0.11111,0.08333,0.05556,0.02778]</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>限制:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code>1 <= n <= 11</code></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
<p>给你两个正整数 <code>left</code> 和 <code>right</code> ,满足 <code>left <= right</code> 。请你计算 <strong>闭区间</strong> <code>[left, right]</code> 中所有整数的 <strong>乘积</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>由于乘积可能非常大,你需要将它按照以下步骤 <strong>缩写</strong> :</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li>统计乘积中 <strong>后缀</strong> 0 的数目,并 <strong>移除</strong> 这些 0 ,将这个数目记为 <code>C</code> 。
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>比方说,<code>1000</code> 中有 <code>3</code> 个后缀 0 ,<code>546</code> 中没有后缀 0 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>将乘积中剩余数字的位数记为 <code>d</code> 。如果 <code>d > 10</code> ,那么将乘积表示为 <code><pre>...<suf></code> 的形式,其中 <code><pre></code> 表示乘积最 <strong>开始</strong> 的 <code>5</code> 个数位,<code><suf></code> 表示删除后缀 0 <strong>之后</strong> 结尾的 <code>5</code> 个数位。如果 <code>d <= 10</code> ,我们不对它做修改。
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>比方说,我们将 <code>1234567654321</code> 表示为 <code>12345...54321</code> ,但是 <code>1234567</code> 仍然表示为 <code>1234567</code> 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>最后,将乘积表示为 <strong>字符串</strong> <code>"<pre>...<suf>eC"</code> 。
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>比方说,<code>12345678987600000</code> 被表示为 <code>"12345...89876e5"</code> 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请你返回一个字符串,表示 <strong>闭区间</strong> <code>[left, right]</code> 中所有整数 <strong>乘积</strong> 的 <strong>缩写</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<b>输入:</b>left = 1, right = 4
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>"24e0"
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
乘积为 1 × 2 × 3 × 4 = 24 。
|
||||
由于没有后缀 0 ,所以 24 保持不变,缩写的结尾为 "e0" 。
|
||||
因为乘积的结果是 2 位数,小于 10 ,所欲我们不进一步将它缩写。
|
||||
所以,最终将乘积表示为 "24e0" 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>left = 2, right = 11
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>"399168e2"
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>乘积为 39916800 。
|
||||
有 2 个后缀 0 ,删除后得到 399168 。缩写的结尾为 "e2" 。
|
||||
删除后缀 0 后是 6 位数,不需要进一步缩写。
|
||||
所以,最终将乘积表示为 "399168e2" 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>left = 371, right = 375
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>"7219856259e3"
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>乘积为 7219856259000 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= left <= right <= 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
20
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/一次编辑 [one-away-lcci].html
Normal file
20
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/一次编辑 [one-away-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
<p>字符串有三种编辑操作:插入一个字符、删除一个字符或者替换一个字符。 给定两个字符串,编写一个函数判定它们是否只需要一次(或者零次)编辑。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>
|
||||
first = "pale"
|
||||
second = "ple"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> True</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>
|
||||
first = "pales"
|
||||
second = "pal"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> False
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
34
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/三合一 [three-in-one-lcci].html
Normal file
34
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/三合一 [three-in-one-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<p>三合一。描述如何只用一个数组来实现三个栈。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>你应该实现<code>push(stackNum, value)</code>、<code>pop(stackNum)</code>、<code>isEmpty(stackNum)</code>、<code>peek(stackNum)</code>方法。<code>stackNum</code>表示栈下标,<code>value</code>表示压入的值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>构造函数会传入一个<code>stackSize</code>参数,代表每个栈的大小。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong> 输入</strong>:
|
||||
["TripleInOne", "push", "push", "pop", "pop", "pop", "isEmpty"]
|
||||
[[1], [0, 1], [0, 2], [0], [0], [0], [0]]
|
||||
<strong> 输出</strong>:
|
||||
[null, null, null, 1, -1, -1, true]
|
||||
<strong>说明</strong>:当栈为空时`pop, peek`返回-1,当栈满时`push`不压入元素。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong> 输入</strong>:
|
||||
["TripleInOne", "push", "push", "push", "pop", "pop", "pop", "peek"]
|
||||
[[2], [0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 3], [0], [0], [0], [0]]
|
||||
<strong> 输出</strong>:
|
||||
[null, null, null, null, 2, 1, -1, -1]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= stackNum <= 2</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
<p>三步问题。有个小孩正在上楼梯,楼梯有n阶台阶,小孩一次可以上1阶、2阶或3阶。实现一种方法,计算小孩有多少种上楼梯的方式。结果可能很大,你需要对结果模1000000007。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> <strong>示例1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong> 输入</strong>:n = 3
|
||||
<strong> 输出</strong>:4
|
||||
<strong> 说明</strong>: 有四种走法
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> <strong>示例2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong> 输入</strong>:n = 5
|
||||
<strong> 输出</strong>:13
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> <strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li>n范围在[1, 1000000]之间</li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
48
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/三角形中最小路径之和 [IlPe0q].html
Normal file
48
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/三角形中最小路径之和 [IlPe0q].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个三角形 <code>triangle</code> ,找出自顶向下的最小路径和。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>每一步只能移动到下一行中相邻的结点上。<strong>相邻的结点 </strong>在这里指的是 <strong>下标</strong> 与 <strong>上一层结点下标</strong> 相同或者等于 <strong>上一层结点下标 + 1</strong> 的两个结点。也就是说,如果正位于当前行的下标 <code>i</code> ,那么下一步可以移动到下一行的下标 <code>i</code> 或 <code>i + 1</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>triangle = [[2],[3,4],[6,5,7],[4,1,8,3]]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>11
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>如下面简图所示:
|
||||
<strong>2</strong>
|
||||
<strong>3</strong> 4
|
||||
6 <strong>5</strong> 7
|
||||
4 <strong>1</strong> 8 3
|
||||
自顶向下的最小路径和为 11(即,2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11)。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>triangle = [[-10]]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>-10
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= triangle.length <= 200</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>triangle[0].length == 1</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>triangle[i].length == triangle[i - 1].length + 1</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>-10<sup>4</sup> <= triangle[i][j] <= 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>进阶:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>你可以只使用 <code>O(n)</code> 的额外空间(<code>n</code> 为三角形的总行数)来解决这个问题吗?</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 120 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/triangle/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/triangle/</a></p>
|
||||
26
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/三除数 [three-divisors].html
Normal file
26
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/三除数 [three-divisors].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个整数 <code>n</code> 。如果 <code>n</code> <strong>恰好有三个正除数</strong> ,返回 <code>true</code><em> </em>;否则,返回<em> </em><code>false</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>如果存在整数 <code>k</code> ,满足 <code>n = k * m</code> ,那么整数 <code>m</code> 就是 <code>n</code> 的一个 <strong>除数</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>n = 2
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>false
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>2 只有两个除数:1 和 2 。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>n = 4
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>true
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>4 有三个除数:1、2 和 4 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n <= 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
22
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/下一个数 [closed-number-lcci].html
Normal file
22
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/下一个数 [closed-number-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
<p>下一个数。给定一个正整数,找出与其二进制表达式中1的个数相同且大小最接近的那两个数(一个略大,一个略小)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> <strong>示例1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong> 输入</strong>:num = 2(或者0b10)
|
||||
<strong> 输出</strong>:[4, 1] 或者([0b100, 0b1])
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> <strong>示例2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong> 输入</strong>:num = 1
|
||||
<strong> 输出</strong>:[2, -1]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> <strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li><code>num</code>的范围在[1, 2147483647]之间;</li>
|
||||
<li>如果找不到前一个或者后一个满足条件的正数,那么输出 -1。</li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
<p>如果整数 <code>x</code> 满足:对于每个数位 <code>d</code> ,这个数位 <strong>恰好</strong> 在 <code>x</code> 中出现 <code>d</code> 次。那么整数 <code>x</code> 就是一个 <strong>数值平衡数</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给你一个整数 <code>n</code> ,请你返回 <strong>严格大于</strong> <code>n</code> 的 <strong>最小数值平衡数</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>n = 1
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>22
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
22 是一个数值平衡数,因为:
|
||||
- 数字 2 出现 2 次
|
||||
这也是严格大于 1 的最小数值平衡数。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>n = 1000
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>1333
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
1333 是一个数值平衡数,因为:
|
||||
- 数字 1 出现 1 次。
|
||||
- 数字 3 出现 3 次。
|
||||
这也是严格大于 1000 的最小数值平衡数。
|
||||
注意,1022 不能作为本输入的答案,因为数字 0 的出现次数超过了 0 。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>n = 3000
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>3133
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
3133 是一个数值平衡数,因为:
|
||||
- 数字 1 出现 1 次。
|
||||
- 数字 3 出现 3 次。
|
||||
这也是严格大于 3000 的最小数值平衡数。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= n <= 10<sup>6</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
34
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/下载插件 [Ju9Xwi].md
Normal file
34
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/下载插件 [Ju9Xwi].md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
小扣打算给自己的 **VS code** 安装使用插件,初始状态下带宽每分钟可以完成 `1` 个插件的下载。假定每分钟选择以下两种策略之一:
|
||||
- 使用当前带宽下载插件
|
||||
- 将带宽加倍(下载插件数量随之加倍)
|
||||
|
||||
请返回小扣完成下载 `n` 个插件最少需要多少分钟。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:实际的下载的插件数量可以超过 `n` 个
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 1:**
|
||||
>输入:`n = 2`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>输出:`2`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>解释:
|
||||
> 以下两个方案,都能实现 2 分钟内下载 2 个插件
|
||||
>- 方案一:第一分钟带宽加倍,带宽可每分钟下载 2 个插件;第二分钟下载 2 个插件
|
||||
>- 方案二:第一分钟下载 1 个插件,第二分钟下载 1 个插件
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 2:**
|
||||
>输入:`n = 4`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>输出:`3`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>解释:
|
||||
> 最少需要 3 分钟可完成 4 个插件的下载,以下是其中一种方案:
|
||||
> 第一分钟带宽加倍,带宽可每分钟下载 2 个插件;
|
||||
> 第二分钟下载 2 个插件;
|
||||
> 第三分钟下载 2 个插件。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**提示:**
|
||||
- `1 <= n <= 10^5`
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个二进制字符串 <code>binary</code> 。 <code>binary</code> 的一个 <strong>子序列</strong> 如果是 <strong>非空</strong> 的且没有 <b>前导</b> <strong>0</strong> (除非数字是 <code>"0"</code> 本身),那么它就是一个 <strong>好</strong> 的子序列。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请你找到 <code>binary</code> <strong>不同好子序列</strong> 的数目。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>比方说,如果 <code>binary = "001"</code> ,那么所有 <strong>好</strong> 子序列为 <code>["0", "0", "1"]</code> ,所以 <b>不同</b> 的好子序列为 <code>"0"</code> 和 <code>"1"</code> 。 注意,子序列 <code>"00"</code> ,<code>"01"</code> 和 <code>"001"</code> 不是好的,因为它们有前导 0 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请你返回 <code>binary</code> 中 <strong>不同好子序列</strong> 的数目。由于答案可能很大,请将它对 <code>10<sup>9</sup> + 7</code> <strong>取余</strong> 后返回。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>一个 <strong>子序列</strong> 指的是从原数组中删除若干个(可以一个也不删除)元素后,不改变剩余元素顺序得到的序列。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>binary = "001"
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>2
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>好的二进制子序列为 ["0", "0", "1"] 。
|
||||
不同的好子序列为 "0" 和 "1" 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>binary = "11"
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>2
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>好的二进制子序列为 ["1", "1", "11"] 。
|
||||
不同的好子序列为 "1" 和 "11" 。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>binary = "101"
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>5
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>好的二进制子序列为 ["1", "0", "1", "10", "11", "101"] 。
|
||||
不同的好子序列为 "0" ,"1" ,"10" ,"11" 和 "101" 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= binary.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>binary</code> 只含有 <code>'0'</code> 和 <code>'1'</code> 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
48
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/不含重复字符的最长子字符串 [wtcaE1].html
Normal file
48
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/不含重复字符的最长子字符串 [wtcaE1].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个字符串 <code>s</code> ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 <strong>最长连续子字符串 </strong>的长度。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>s = "abcabcbb"
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>3
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong> 因为无重复字符的最长子字符串是 <code>"abc",所以其</code>长度为 3。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>s = "bbbbb"
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>1
|
||||
<strong>解释: </strong>因为无重复字符的最长子字符串是 <code>"b"</code>,所以其长度为 1。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>s = "pwwkew"
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>3
|
||||
<strong>解释: </strong>因为无重复字符的最长子串是 <code>"wke"</code>,所以其长度为 3。
|
||||
请注意,你的答案必须是 <strong>子串 </strong>的长度,<code>"pwke"</code> 是一个<em>子序列,</em>不是子串。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 4:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>s = ""
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>0
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= s.length <= 5 * 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>s</code> 由英文字母、数字、符号和空格组成</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 3 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
<p>写一个函数,求两个整数之和,要求在函数体内不得使用 “+”、“-”、“*”、“/” 四则运算符号。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> a = 1, b = 1
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 2</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>a</code>, <code>b</code> 均可能是负数或 0</li>
|
||||
<li>结果不会溢出 32 位整数</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<p>设计一个函数把两个数字相加。不得使用 + 或者其他算术运算符。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> a = 1, b = 1
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 2</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>a</code>, <code>b</code> 均可能是负数或 0</li>
|
||||
<li>结果不会溢出 32 位整数</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
18
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/丑数 [chou-shu-lcof].html
Normal file
18
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/丑数 [chou-shu-lcof].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
<p>我们把只包含质因子 2、3 和 5 的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。求按从小到大的顺序的第 n 个丑数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> n = 10
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 12
|
||||
<strong>解释: </strong><code>1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12</code> 是前 10 个丑数。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>说明: </strong> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li><code>1</code> 是丑数。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>n</code> <strong>不超过</strong>1690。</li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意:本题与主站 264 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ugly-number-ii/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ugly-number-ii/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
<p>表: <code>Employees</code></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
+-------------+---------+
|
||||
| Column Name | Type |
|
||||
+-------------+---------+
|
||||
| employee_id | int |
|
||||
| name | varchar |
|
||||
+-------------+---------+
|
||||
employee_id 是这个表的主键。
|
||||
每一行表示雇员的id 和他的姓名。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>表: <code>Salaries</code></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
+-------------+---------+
|
||||
| Column Name | Type |
|
||||
+-------------+---------+
|
||||
| employee_id | int |
|
||||
| salary | int |
|
||||
+-------------+---------+
|
||||
employee_id is 这个表的主键。
|
||||
每一行表示雇员的id 和他的薪水。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>写出一个查询语句,找到所有 <strong>丢失信息</strong> 的雇员id。当满足下面一个条件时,就被认为是雇员的信息丢失:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>雇员的 <strong>姓名</strong> 丢失了,或者</li>
|
||||
<li>雇员的 <strong>薪水信息</strong> 丢失了,或者</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回这些雇员的id <code>employee_id</code> , <strong>从小到大排序 </strong>。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>查询结果格式如下面的例子所示。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>
|
||||
Employees table:
|
||||
+-------------+----------+
|
||||
| employee_id | name |
|
||||
+-------------+----------+
|
||||
| 2 | Crew |
|
||||
| 4 | Haven |
|
||||
| 5 | Kristian |
|
||||
+-------------+----------+
|
||||
Salaries table:
|
||||
+-------------+--------+
|
||||
| employee_id | salary |
|
||||
+-------------+--------+
|
||||
| 5 | 76071 |
|
||||
| 1 | 22517 |
|
||||
| 4 | 63539 |
|
||||
+-------------+--------+
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>
|
||||
+-------------+
|
||||
| employee_id |
|
||||
+-------------+
|
||||
| 1 |
|
||||
| 2 |
|
||||
+-------------+
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
雇员1,2,4,5 都工作在这个公司。
|
||||
1号雇员的姓名丢失了。
|
||||
2号雇员的薪水信息丢失了。</pre>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个字符串 <code>s</code> ,请你找到 <code>s</code> 中两个 <strong>不相交回文子序列</strong> ,使得它们长度的 <strong>乘积最大</strong> 。两个子序列在原字符串中如果没有任何相同下标的字符,则它们是 <strong>不相交</strong> 的。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请你返回两个回文子序列长度可以达到的<strong> 最大乘积</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>子序列</strong> 指的是从原字符串中删除若干个字符(可以一个也不删除)后,剩余字符不改变顺序而得到的结果。如果一个字符串从前往后读和从后往前读一模一样,那么这个字符串是一个 <strong>回文字符串</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="example-1" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/08/24/two-palindromic-subsequences.png" style="width: 550px; height: 124px;"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>s = "leetcodecom"
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>9
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>最优方案是选择 "ete" 作为第一个子序列,"cdc" 作为第二个子序列。
|
||||
它们的乘积为 3 * 3 = 9 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>s = "bb"
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>1
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>最优方案为选择 "b" (第一个字符)作为第一个子序列,"b" (第二个字符)作为第二个子序列。
|
||||
它们的乘积为 1 * 1 = 1 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>s = "accbcaxxcxx"
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>25
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>最优方案为选择 "accca" 作为第一个子序列,"xxcxx" 作为第二个子序列。
|
||||
它们的乘积为 5 * 5 = 25 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>2 <= s.length <= 12</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>s</code> 只含有小写英文字母。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的二维整数数组 <code>events</code> ,其中 <code>events[i] = [startTime<sub>i</sub>, endTime<sub>i</sub>, value<sub>i</sub>]</code> 。第 <code>i</code> 个活动开始于 <code>startTime<sub>i</sub></code> ,结束于 <code>endTime<sub>i</sub></code> ,如果你参加这个活动,那么你可以得到价值 <code>value<sub>i</sub></code> 。你 <strong>最多</strong> 可以参加 <strong>两个时间不重叠</strong> 活动,使得它们的价值之和 <strong>最大</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请你返回价值之和的 <strong>最大值</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意,活动的开始时间和结束时间是 <strong>包括</strong> 在活动时间内的,也就是说,你不能参加两个活动且它们之一的开始时间等于另一个活动的结束时间。更具体的,如果你参加一个活动,且结束时间为 <code>t</code> ,那么下一个活动必须在 <code>t + 1</code> 或之后的时间开始。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/09/21/picture5.png" style="width: 400px; height: 75px;"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>events = [[1,3,2],[4,5,2],[2,4,3]]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>4
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>选择绿色的活动 0 和 1 ,价值之和为 2 + 2 = 4 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="Example 1 Diagram" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/09/21/picture1.png" style="width: 400px; height: 77px;"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>events = [[1,3,2],[4,5,2],[1,5,5]]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>5
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>选择活动 2 ,价值和为 5 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/09/21/picture3.png" style="width: 400px; height: 66px;"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>events = [[1,5,3],[1,5,1],[6,6,5]]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>8
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>选择活动 0 和 2 ,价值之和为 3 + 5 = 8 。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>2 <= events.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>events[i].length == 3</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= startTime<sub>i</sub> <= endTime<sub>i</sub> <= 10<sup>9</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= value<sub>i</sub> <= 10<sup>6</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
给你两个 <strong>从小到大排好序</strong> 且下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的整数数组 <code>nums1</code> 和 <code>nums2</code> 以及一个整数 <code>k</code> ,请你返回第<em> </em><code>k</code> (从 <strong>1</strong> 开始编号)小的 <code>nums1[i] * nums2[j]</code><em> </em>的乘积,其中<em> </em><code>0 <= i < nums1.length</code><em> </em>且<em> </em><code>0 <= j < nums2.length</code> 。
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>nums1 = [2,5], nums2 = [3,4], k = 2
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>8
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>第 2 小的乘积计算如下:
|
||||
- nums1[0] * nums2[0] = 2 * 3 = 6
|
||||
- nums1[0] * nums2[1] = 2 * 4 = 8
|
||||
第 2 小的乘积为 8 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>nums1 = [-4,-2,0,3], nums2 = [2,4], k = 6
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>0
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>第 6 小的乘积计算如下:
|
||||
- nums1[0] * nums2[1] = (-4) * 4 = -16
|
||||
- nums1[0] * nums2[0] = (-4) * 2 = -8
|
||||
- nums1[1] * nums2[1] = (-2) * 4 = -8
|
||||
- nums1[1] * nums2[0] = (-2) * 2 = -4
|
||||
- nums1[2] * nums2[0] = 0 * 2 = 0
|
||||
- nums1[2] * nums2[1] = 0 * 4 = 0
|
||||
第 6 小的乘积为 0 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>nums1 = [-2,-1,0,1,2], nums2 = [-3,-1,2,4,5], k = 3
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>-6
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>第 3 小的乘积计算如下:
|
||||
- nums1[0] * nums2[4] = (-2) * 5 = -10
|
||||
- nums1[0] * nums2[3] = (-2) * 4 = -8
|
||||
- nums1[4] * nums2[0] = 2 * (-3) = -6
|
||||
第 3 小的乘积为 -6 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 5 * 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>-10<sup>5</sup> <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= k <= nums1.length * nums2.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>nums1</code> 和 <code>nums2</code> 都是从小到大排好序的。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
<p>输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>如下面的两个链表<strong>:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><a href="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/160_statement.png" target="_blank"><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/160_statement.png" style="height: 130px; width: 400px;"></a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在节点 c1 开始相交。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><a href="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2018/12/13/160_example_1.png" target="_blank"><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/160_example_1.png" style="height: 130px; width: 400px;"></a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>Reference of the node with value = 8
|
||||
<strong>输入解释:</strong>相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><a href="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2018/12/13/160_example_2.png" target="_blank"><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/160_example_2.png" style="height: 136px; width: 350px;"></a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>Reference of the node with value = 2
|
||||
<strong>输入解释:</strong>相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><a href="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2018/12/13/160_example_3.png" target="_blank"><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/160_example_3.png" style="height: 126px; width: 200px;"></a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>null
|
||||
<strong>输入解释:</strong>从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>注意:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>如果两个链表没有交点,返回 <code>null</code>.</li>
|
||||
<li>在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。</li>
|
||||
<li>可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。</li>
|
||||
<li>程序尽量满足 O(<em>n</em>) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(<em>1</em>) 内存。</li>
|
||||
<li>本题与主站 160 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/</a></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
70
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/两个链表的第一个重合节点 [3u1WK4].html
Normal file
70
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/两个链表的第一个重合节点 [3u1WK4].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
<p>给定两个单链表的头节点 <code>headA</code> 和 <code>headB</code> ,请找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 <code>null</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>图示两个链表在节点 <code>c1</code> 开始相交<strong>:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><a href="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/160_statement.png" target="_blank"><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/160_statement.png" style="height: 130px; width: 400px;" /></a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>题目数据 <strong>保证</strong> 整个链式结构中不存在环。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>注意</strong>,函数返回结果后,链表必须 <strong>保持其原始结构</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><a href="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2018/12/13/160_example_1.png" target="_blank"><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/160_example_1.png" style="height: 130px; width: 400px;" /></a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>Intersected at '8'
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
|
||||
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
|
||||
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><a href="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2018/12/13/160_example_2.png" target="_blank"><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/160_example_2.png" style="height: 136px; width: 350px;" /></a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>Intersected at '2'
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
|
||||
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
|
||||
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><a href="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2018/12/13/160_example_3.png" target="_blank"><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/160_example_3.png" style="height: 126px; width: 200px;" /></a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>null
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
|
||||
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
|
||||
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>listA</code> 中节点数目为 <code>m</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>listB</code> 中节点数目为 <code>n</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= m, n <= 3 * 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= Node.val <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= skipA <= m</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= skipB <= n</code></li>
|
||||
<li>如果 <code>listA</code> 和 <code>listB</code> 没有交点,<code>intersectVal</code> 为 <code>0</code></li>
|
||||
<li>如果 <code>listA</code> 和 <code>listB</code> 有交点,<code>intersectVal == listA[skipA + 1] == listB[skipB + 1]</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>进阶:</strong>能否设计一个时间复杂度 <code>O(n)</code> 、仅用 <code>O(1)</code> 内存的解决方案?</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 160 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
<p>街上有 <code>n</code> 栋房子整齐地排成一列,每栋房子都粉刷上了漂亮的颜色。给你一个下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始且长度为 <code>n</code> 的整数数组 <code>colors</code> ,其中 <code>colors[i]</code> 表示第 <code>i</code> 栋房子的颜色。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回 <strong>两栋</strong> 颜色 <strong>不同</strong> 房子之间的 <strong>最大</strong> 距离。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>第 <code>i</code> 栋房子和第 <code>j</code> 栋房子之间的距离是 <code>abs(i - j)</code> ,其中 <code>abs(x)</code> 是 <code>x</code> 的绝对值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/10/31/eg1.png" style="width: 610px; height: 84px;" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>colors = [<strong><em>1</em></strong>,1,1,<em><strong>6</strong></em>,1,1,1]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>3
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>上图中,颜色 1 标识成蓝色,颜色 6 标识成红色。
|
||||
两栋颜色不同且距离最远的房子是房子 0 和房子 3 。
|
||||
房子 0 的颜色是颜色 1 ,房子 3 的颜色是颜色 6 。两栋房子之间的距离是 abs(0 - 3) = 3 。
|
||||
注意,房子 3 和房子 6 也可以产生最佳答案。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/10/31/eg2.png" style="width: 426px; height: 84px;" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>colors = [<em><strong>1</strong></em>,8,3,8,<em><strong>3</strong></em>]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>4
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>上图中,颜色 1 标识成蓝色,颜色 8 标识成黄色,颜色 3 标识成绿色。
|
||||
两栋颜色不同且距离最远的房子是房子 0 和房子 4 。
|
||||
房子 0 的颜色是颜色 1 ,房子 4 的颜色是颜色 3 。两栋房子之间的距离是 abs(0 - 4) = 4 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>colors = [<em><strong>0</strong></em>,<em><strong>1</strong></em>]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>1
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>两栋颜色不同且距离最远的房子是房子 0 和房子 1 。
|
||||
房子 0 的颜色是颜色 0 ,房子 1 的颜色是颜色 1 。两栋房子之间的距离是 abs(0 - 1) = 1 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>n == colors.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>2 <= n <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= colors[i] <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li>生成的测试数据满足 <strong>至少 </strong>存在 2 栋颜色不同的房子</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
<p>数组中占比超过一半的元素称之为主要元素。给你一个<strong> 整数 </strong>数组,找出其中的主要元素。若没有,返回 <code>-1</code> 。请设计时间复杂度为 <code>O(N)</code> 、空间复杂度为 <code>O(1)</code> 的解决方案。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>[1,2,5,9,5,9,5,5,5]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>5</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>[3,2]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>-1</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>[2,2,1,1,1,2,2]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>2</pre>
|
||||
27
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/主题空间 [YesdPw].md
Normal file
27
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/主题空间 [YesdPw].md
Normal file
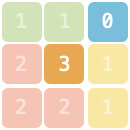
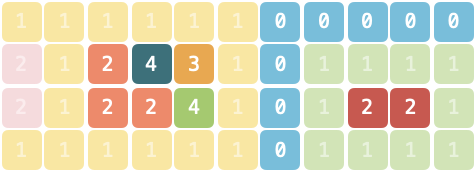
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
「以扣会友」线下活动所在场地由若干主题空间与走廊组成,场地的地图记作由一维字符串型数组 `grid`,字符串中仅包含 `"0"~"5"` 这 6 个字符。地图上每一个字符代表面积为 1 的区域,其中 `"0"` 表示走廊,其他字符表示主题空间。相同且连续(连续指上、下、左、右四个方向连接)的字符组成同一个主题空间。
|
||||
|
||||
假如整个 `grid` 区域的外侧均为走廊。请问,不与走廊直接相邻的主题空间的最大面积是多少?如果不存在这样的空间请返回 `0`。
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 1:**
|
||||
>输入:`grid = ["110","231","221"]`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>输出:`1`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>解释:4 个主题空间中,只有 1 个不与走廊相邻,面积为 1。
|
||||
>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 2:**
|
||||
>输入:`grid = ["11111100000","21243101111","21224101221","11111101111"]`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>输出:`3`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>解释:8 个主题空间中,有 5 个不与走廊相邻,面积分别为 3、1、1、1、2,最大面积为 3。
|
||||
>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**提示:**
|
||||
- `1 <= grid.length <= 500`
|
||||
- `1 <= grid[i].length <= 500`
|
||||
- `grid[i][j]` 仅可能是 `"0"~"5"`
|
||||
|
||||
30
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/乐团站位 [SNJvJP].md
Normal file
30
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/乐团站位 [SNJvJP].md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
某乐团的演出场地可视作 `num * num` 的二维矩阵 `grid`(左上角坐标为 `[0,0]`),每个位置站有一位成员。乐团共有 `9` 种乐器,乐器编号为 `1~9`,每位成员持有 `1` 个乐器。
|
||||
|
||||
为保证声乐混合效果,成员站位规则为:自 `grid` 左上角开始顺时针螺旋形向内循环以 `1,2,...,9` 循环重复排列。例如当 num = `5` 时,站位如图所示
|
||||
|
||||
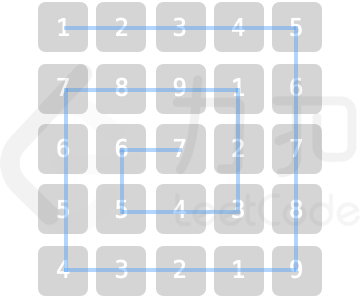
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
请返回位于场地坐标 [`Xpos`,`Ypos`] 的成员所持乐器编号。
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 1:**
|
||||
>输入:`num = 3, Xpos = 0, Ypos = 2`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>输出:`3`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>解释:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 2:**
|
||||
>输入:`num = 4, Xpos = 1, Ypos = 2`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>输出:`5`
|
||||
>
|
||||
>解释:
|
||||
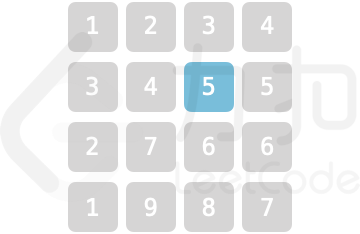
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**提示:**
|
||||
- `1 <= num <= 10^9`
|
||||
- `0 <= Xpos, Ypos < num`
|
||||
32
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/乘积小于 K 的子数组 [ZVAVXX].html
Normal file
32
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/乘积小于 K 的子数组 [ZVAVXX].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个正整数数组 <code>nums</code>和整数 <code>k</code> ,请找出该数组内乘积小于 <code>k</code> 的连续的子数组的个数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> nums = [10,5,2,6], k = 100
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 8
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong> 8 个乘积小于 100 的子数组分别为: [10], [5], [2], [6], [10,5], [5,2], [2,6], [5,2,6]。
|
||||
需要注意的是 [10,5,2] 并不是乘积小于100的子数组。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> nums = [1,2,3], k = 0
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 0</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示: </strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums[i] <= 1000</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= k <= 10<sup>6</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 713 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subarray-product-less-than-k/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subarray-product-less-than-k/</a> </p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
<p>有 <code>n</code> 个人前来排队买票,其中第 <code>0</code> 人站在队伍 <strong>最前方</strong> ,第 <code>(n - 1)</code> 人站在队伍 <strong>最后方</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给你一个下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的整数数组 <code>tickets</code> ,数组长度为 <code>n</code> ,其中第 <code>i</code> 人想要购买的票数为 <code>tickets[i]</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>每个人买票都需要用掉 <strong>恰好 1 秒</strong> 。一个人 <strong>一次只能买一张票</strong> ,如果需要购买更多票,他必须走到 <strong>队尾</strong> 重新排队(<strong>瞬间 </strong>发生,不计时间)。如果一个人没有剩下需要买的票,那他将会 <strong>离开</strong> 队伍。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回位于位置 <code>k</code>(下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始)的人完成买票需要的时间(以秒为单位)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>tickets = [2,3,2], k = 2
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>6
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
- 第一轮,队伍中的每个人都买到一张票,队伍变为 [1, 2, 1] 。
|
||||
- 第二轮,队伍中的每个都又都买到一张票,队伍变为 [0, 1, 0] 。
|
||||
位置 2 的人成功买到 2 张票,用掉 3 + 3 = 6 秒。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>tickets = [5,1,1,1], k = 0
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>8
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
- 第一轮,队伍中的每个人都买到一张票,队伍变为 [4, 0, 0, 0] 。
|
||||
- 接下来的 4 轮,只有位置 0 的人在买票。
|
||||
位置 0 的人成功买到 5 张票,用掉 4 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 8 秒。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>n == tickets.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= tickets[i] <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= k < n</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
52
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二分图 [vEAB3K].html
Normal file
52
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二分图 [vEAB3K].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
<p>存在一个 <strong>无向图</strong> ,图中有 <code>n</code> 个节点。其中每个节点都有一个介于 <code>0</code> 到 <code>n - 1</code> 之间的唯一编号。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给定一个二维数组 <code>graph</code> ,表示图,其中 <code>graph[u]</code> 是一个节点数组,由节点 <code>u</code> 的邻接节点组成。形式上,对于 <code>graph[u]</code> 中的每个 <code>v</code> ,都存在一条位于节点 <code>u</code> 和节点 <code>v</code> 之间的无向边。该无向图同时具有以下属性:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>不存在自环(<code>graph[u]</code> 不包含 <code>u</code>)。</li>
|
||||
<li>不存在平行边(<code>graph[u]</code> 不包含重复值)。</li>
|
||||
<li>如果 <code>v</code> 在 <code>graph[u]</code> 内,那么 <code>u</code> 也应该在 <code>graph[v]</code> 内(该图是无向图)</li>
|
||||
<li>这个图可能不是连通图,也就是说两个节点 <code>u</code> 和 <code>v</code> 之间可能不存在一条连通彼此的路径。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>二分图</strong> 定义:如果能将一个图的节点集合分割成两个独立的子集 <code>A</code> 和 <code>B</code> ,并使图中的每一条边的两个节点一个来自 <code>A</code> 集合,一个来自 <code>B</code> 集合,就将这个图称为 <strong>二分图</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>如果图是二分图,返回 <code>true</code><em> </em>;否则,返回 <code>false</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2020/10/21/bi2.jpg" style="width: 222px; height: 222px;" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>graph = [[1,2,3],[0,2],[0,1,3],[0,2]]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>false
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong><code>不能将节点分割成两个独立的子集,</code>以使每条边都连通一个子集中的一个节点与另一个子集中的一个节点。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2020/10/21/bi1.jpg" style="width: 222px; height: 222px;" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>graph = [[1,3],[0,2],[1,3],[0,2]]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>true
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong><code>可以将节点分成两组: {0, 2} 和 {1, 3} 。</code></pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>graph.length == n</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= graph[u].length < n</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= graph[u][i] <= n - 1</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>graph[u]</code> 不会包含 <code>u</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>graph[u]</code> 的所有值 <strong>互不相同</strong></li>
|
||||
<li>如果 <code>graph[u]</code> 包含 <code>v</code>,那么 <code>graph[v]</code> 也会包含 <code>u</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 785 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/is-graph-bipartite/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/is-graph-bipartite/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
<p>输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的循环双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的节点,只能调整树中节点指针的指向。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>为了让您更好地理解问题,以下面的二叉搜索树为例:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2018/10/12/bstdlloriginalbst.png"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>我们希望将这个二叉搜索树转化为双向循环链表。链表中的每个节点都有一个前驱和后继指针。对于双向循环链表,第一个节点的前驱是最后一个节点,最后一个节点的后继是第一个节点。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>下图展示了上面的二叉搜索树转化成的链表。“head” 表示指向链表中有最小元素的节点。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2018/10/12/bstdllreturndll.png"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>特别地,我们希望可以就地完成转换操作。当转化完成以后,树中节点的左指针需要指向前驱,树中节点的右指针需要指向后继。还需要返回链表中的第一个节点的指针。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>注意:</strong>本题与主站 426 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-binary-search-tree-to-sorted-doubly-linked-list/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-binary-search-tree-to-sorted-doubly-linked-list/</a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>注意:</strong>此题对比原题有改动。</p>
|
||||
34
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉搜索树中两个节点之和 [opLdQZ].html
Normal file
34
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉搜索树中两个节点之和 [opLdQZ].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个二叉搜索树的 <strong>根节点</strong> <code>root</code> 和一个整数 <code>k</code> , 请判断该二叉搜索树中是否存在两个节点它们的值之和等于 <code>k</code> 。假设二叉搜索树中节点的值均唯一。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>root =<strong> </strong>[8,6,10,5,7,9,11], k = 12
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>true
|
||||
<strong>解释: </strong>节点 5 和节点 7 之和等于 12
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>root =<strong> </strong>[8,6,10,5,7,9,11], k = 22
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>false
|
||||
<strong>解释: </strong>不存在两个节点值之和为 22 的节点
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>二叉树的节点个数的范围是 <code>[1, 10<sup>4</sup>]</code>.</li>
|
||||
<li><code>-10<sup>4</sup> <= Node.val <= 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>root</code> 为二叉搜索树</li>
|
||||
<li><code>-10<sup>5</sup> <= k <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意:本题与主站 653 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum-iv-input-is-a-bst/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum-iv-input-is-a-bst/</a></p>
|
||||
39
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉搜索树中的中序后继 [P5rCT8].html
Normal file
39
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉搜索树中的中序后继 [P5rCT8].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一棵二叉搜索树和其中的一个节点 <code>p</code> ,找到该节点在树中的中序后继。如果节点没有中序后继,请返回 <code>null</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>节点 <code>p</code> 的后继是值比 <code>p.val</code> 大的节点中键值最小的节点,即按中序遍历的顺序节点 <code>p</code> 的下一个节点。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2019/01/23/285_example_1.PNG" style="height: 117px; width: 122px;" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>root = [2,1,3], p = 1
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>2
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>这里 1 的中序后继是 2。请注意 p 和返回值都应是 TreeNode 类型。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2019/01/23/285_example_2.PNG" style="height: 229px; width: 246px;" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], p = 6
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>null
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>因为给出的节点没有中序后继,所以答案就返回 <code>null 了。</code>
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>树中节点的数目在范围 <code>[1, 10<sup>4</sup>]</code> 内。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>-10<sup>5</sup> <= Node.val <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li>树中各节点的值均保证唯一。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 285 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/inorder-successor-in-bst/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/inorder-successor-in-bst/</a></p>
|
||||
37
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉搜索树序列 [bst-sequences-lcci].html
Normal file
37
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉搜索树序列 [bst-sequences-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
<p>从左向右遍历一个数组,通过不断将其中的元素插入树中可以逐步地生成一棵二叉搜索树。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给定一个由<strong>不同节点</strong>组成的二叉搜索树 <code>root</code>,输出所有可能生成此树的数组。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>root = [2,1,3]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[[2,1,3],[2,3,1]]
|
||||
解释: 数组 [2,1,3]、[2,3,1] 均可以通过从左向右遍历元素插入树中形成以下二叉搜索树
|
||||
2
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
1 3
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例</strong><strong> 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>root = [4,1,null,null,3,2]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[[4,1,3,2]]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>二叉搜索树中的节点数在<meta charset="UTF-8" /> <code>[0, 1000]</code> 的范围内</li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= 节点值 <= 10^6</code></li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<p>用例保证符合要求的数组数量不超过 <code>5000</code></p>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
<p>输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历结果。如果是则返回 <code>true</code>,否则返回 <code>false</code>。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>参考以下这颗二叉搜索树:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre> 5
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
2 6
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
1 3</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入: </strong>[1,6,3,2,5]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>false</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入: </strong>[1,3,2,6,5]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>true</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li><code>数组长度 <= 1000</code></li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><a href="https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%9C%80%E8%BF%91%E5%85%AC%E5%85%B1%E7%A5%96%E5%85%88/8918834?fr=aladdin" target="_blank">百度百科</a>中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(<strong>一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先</strong>)。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/binarysearchtree_improved.png"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 6
|
||||
<strong>解释: </strong>节点 <code>2 </code>和节点 <code>8 </code>的最近公共祖先是 <code>6。</code>
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 2
|
||||
<strong>解释: </strong>节点 <code>2</code> 和节点 <code>4</code> 的最近公共祖先是 <code>2</code>, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>说明:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>所有节点的值都是唯一的。</li>
|
||||
<li>p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意:本题与主站 235 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中第 <code>k</code> 大的节点的值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
|
||||
3
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
1 4
|
||||
\
|
||||
2
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 4</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
|
||||
5
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
3 6
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
2 4
|
||||
/
|
||||
1
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 4</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>限制:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>1 ≤ k ≤ 二叉搜索树元素个数</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
63
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉搜索树迭代器 [kTOapQ].html
Normal file
63
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉搜索树迭代器 [kTOapQ].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
<p>实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器类<code>BSTIterator</code> ,表示一个按中序遍历二叉搜索树(BST)的迭代器:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="original__bRMd">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>BSTIterator(TreeNode root)</code> 初始化 <code>BSTIterator</code> 类的一个对象。BST 的根节点 <code>root</code> 会作为构造函数的一部分给出。指针应初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,且该数字小于 BST 中的任何元素。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>boolean hasNext()</code> 如果向指针右侧遍历存在数字,则返回 <code>true</code> ;否则返回 <code>false</code> 。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>int next()</code>将指针向右移动,然后返回指针处的数字。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意,指针初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,所以对 <code>next()</code> 的首次调用将返回 BST 中的最小元素。</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>可以假设 <code>next()</code> 调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用 <code>next()</code> 时,BST 的中序遍历中至少存在一个下一个数字。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2018/12/25/bst-tree.png" style="width: 189px; height: 178px;" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入</strong>
|
||||
inputs = ["BSTIterator", "next", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"]
|
||||
inputs = [[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []]
|
||||
<strong>输出</strong>
|
||||
[null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false]
|
||||
|
||||
<strong>解释</strong>
|
||||
BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]);
|
||||
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 3
|
||||
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 7
|
||||
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
|
||||
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 9
|
||||
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
|
||||
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 15
|
||||
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
|
||||
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 20
|
||||
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 False
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>树中节点的数目在范围 <code>[1, 10<sup>5</sup>]</code> 内</li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= Node.val <= 10<sup>6</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li>最多调用 <code>10<sup>5</sup></code> 次 <code>hasNext</code> 和 <code>next</code> 操作</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>进阶:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>你可以设计一个满足下述条件的解决方案吗?<code>next()</code> 和 <code>hasNext()</code> 操作均摊时间复杂度为 <code>O(1)</code> ,并使用 <code>O(h)</code> 内存。其中 <code>h</code> 是树的高度。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 173 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search-tree-iterator/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search-tree-iterator/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
<p>给你二叉树的根节点 <code>root</code> 和一个整数目标和 <code>targetSum</code> ,找出所有 <strong>从根节点到叶子节点</strong> 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>叶子节点</strong> 是指没有子节点的节点。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/01/18/pathsumii1.jpg" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/01/18/pathsum2.jpg" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>[]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>[]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>树中节点总数在范围 <code>[0, 5000]</code> 内</li>
|
||||
<li><code>-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意:本题与主站 113 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum-ii/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum-ii/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
<p>任务调度优化是计算机性能优化的关键任务之一。在任务众多时,不同的调度策略可能会得到不同的总体执行时间,因此寻求一个最优的调度方案是非常有必要的。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>通常任务之间是存在依赖关系的,即对于某个任务,你需要先<strong>完成</strong>他的前导任务(如果非空),才能开始执行该任务。<strong>我们保证任务的依赖关系是一棵二叉树,</strong>其中 <code>root</code> 为根任务,<code>root.left</code> 和 <code>root.right</code> 为他的两个前导任务(可能为空),<code>root.val</code> 为其自身的执行时间。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在一个 CPU 核执行某个任务时,我们可以在任何时刻暂停当前任务的执行,并保留当前执行进度。在下次继续执行该任务时,会从之前停留的进度开始继续执行。暂停的时间可以不是整数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>现在,系统有<strong>两个</strong> CPU 核,即我们可以同时执行两个任务,但是同一个任务不能同时在两个核上执行。给定这颗任务树,请求出所有任务执行完毕的最小时间。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>
|
||||
<p><img alt="image.png" src="https://pic.leetcode-cn.com/3522fbf8ce4ebb20b79019124eb9870109fdfe97fe9da99f6c20c07ceb1c60b3-image.png" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>输入:root = [47, 74, 31]</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>输出:121</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>解释:根节点的左右节点可以并行执行31分钟,剩下的43+47分钟只能串行执行,因此总体执行时间是121分钟。</p>
|
||||
</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>
|
||||
<p><img alt="image.png" src="https://pic.leetcode-cn.com/13accf172ee4a660d241e25901595d55b759380b090890a17e6e7bd51a143e3f-image.png" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>输入:root = [15, 21, null, 24, null, 27, 26]</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>输出:87</p>
|
||||
</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>
|
||||
<p><img alt="image.png" src="https://pic.leetcode-cn.com/bef743a12591aafb9047dd95d335b8083dfa66e8fdedc63f50fd406b4a9d163a-image.png" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>输入:root = [1,3,2,null,null,4,4]</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>输出:7.5</p>
|
||||
</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>限制:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= 节点数量 <= 1000</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= 单节点执行时间 <= 1000</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
50
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉树剪枝 [pOCWxh].html
Normal file
50
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉树剪枝 [pOCWxh].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个二叉树 <strong>根节点</strong> <code>root</code> ,树的每个节点的值要么是 <code>0</code>,要么是 <code>1</code>。请剪除该二叉树中所有节点的值为 <code>0</code> 的子树。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>节点 <code>node</code> 的子树为 <code>node</code> 本身,以及所有 <code>node</code> 的后代。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> [1,null,0,0,1]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[1,null,0,null,1]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
只有红色节点满足条件“所有不包含 1 的子树”。
|
||||
右图为返回的答案。
|
||||
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://s3-lc-upload.s3.amazonaws.com/uploads/2018/04/06/1028_2.png" style="width:450px" />
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> [1,0,1,0,0,0,1]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[1,null,1,null,1]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://s3-lc-upload.s3.amazonaws.com/uploads/2018/04/06/1028_1.png" style="width:450px" />
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> [1,1,0,1,1,0,1,0]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[1,1,0,1,1,null,1]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://s3-lc-upload.s3.amazonaws.com/uploads/2018/04/05/1028.png" style="width:450px" />
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>二叉树的节点个数的范围是 <code>[1,200]</code></li>
|
||||
<li>二叉树节点的值只会是 <code>0</code> 或 <code>1</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 814 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-pruning/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-pruning/</a></p>
|
||||
36
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉树最底层最左边的值 [LwUNpT].html
Normal file
36
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉树最底层最左边的值 [LwUNpT].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个二叉树的 <strong>根节点</strong> <code>root</code>,请找出该二叉树的 <strong>最底层 最左边 </strong>节点的值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2020/12/14/tree1.jpg" style="width: 182px; " /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>root = [2,1,3]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>1
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2: </strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2020/12/14/tree2.jpg" style="width: 242px; " /><strong> </strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>[1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>7
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>二叉树的节点个数的范围是 <code>[1,10<sup>4</sup>]</code></li>
|
||||
<li><meta charset="UTF-8" /><code>-2<sup>31</sup> <= Node.val <= 2<sup>31</sup> - 1</code> </li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 513 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/</a></p>
|
||||
27
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉树染色 [er-cha-shu-ran-se-UGC].md
Normal file
27
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉树染色 [er-cha-shu-ran-se-UGC].md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
小扣有一个根结点为 `root` 的二叉树模型,初始所有结点均为白色,可以用蓝色染料给模型结点染色,模型的每个结点有一个 `val` 价值。小扣出于美观考虑,希望最后二叉树上每个蓝色相连部分的结点个数不能超过 `k` 个,求所有染成蓝色的结点价值总和最大是多少?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 1:**
|
||||
> 输入:`root = [5,2,3,4], k = 2`
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 输出:`12`
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 解释:`结点 5、3、4 染成蓝色,获得最大的价值 5+3+4=12`
|
||||
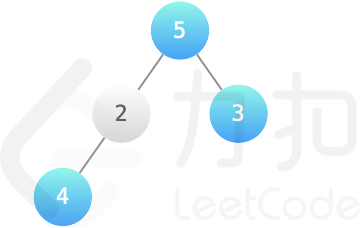
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**示例 2:**
|
||||
> 输入:`root = [4,1,3,9,null,null,2], k = 2`
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 输出:`16`
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 解释:结点 4、3、9 染成蓝色,获得最大的价值 4+3+9=16
|
||||
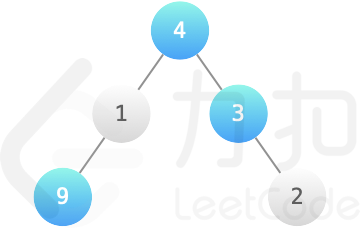
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**提示:**
|
||||
+ `1 <= k <= 10`
|
||||
+ `1 <= val <= 10000`
|
||||
+ `1 <= 结点数量 <= 10000`
|
||||
|
||||
65
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉树每层的最大值 [hPov7L].html
Normal file
65
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉树每层的最大值 [hPov7L].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一棵二叉树的根节点 <code>root</code> ,请找出该二叉树中每一层的最大值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[1,3,9]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
1
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
3 2
|
||||
/ \ \
|
||||
5 3 9
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>root = [1,2,3]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[1,3]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
1
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
2 3
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>root = [1]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[1]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例4:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>root = [1,null,2]
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[1,2]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
1
|
||||
\
|
||||
2
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例5:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>root = []
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>二叉树的节点个数的范围是 <code>[0,10<sup>4</sup>]</code></li>
|
||||
<li><meta charset="UTF-8" /><code>-2<sup>31</sup> <= Node.val <= 2<sup>31</sup> - 1</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 515 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-largest-value-in-each-tree-row/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-largest-value-in-each-tree-row/</a></p>
|
||||
39
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉树的右侧视图 [WNC0Lk].html
Normal file
39
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二叉树的右侧视图 [WNC0Lk].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个二叉树的 <strong>根节点</strong> <code>root</code>,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/02/14/tree.jpg" style="width: 270px; " /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> [1,3,4]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> [1,null,3]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> [1,3]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> []
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> []
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>二叉树的节点个数的范围是 <code>[0,100]</code></li>
|
||||
<li><meta charset="UTF-8" /><code>-100 <= Node.val <= 100</code> </li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 199 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><a href="https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%9C%80%E8%BF%91%E5%85%AC%E5%85%B1%E7%A5%96%E5%85%88/8918834?fr=aladdin" target="_blank">百度百科</a>中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(<strong>一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先</strong>)。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode-cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/15/binarytree.png"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 3
|
||||
<strong>解释: </strong>节点 <code>5 </code>和节点 <code>1 </code>的最近公共祖先是节点 <code>3。</code>
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> 5
|
||||
<strong>解释: </strong>节点 <code>5 </code>和节点 <code>4 </code>的最近公共祖先是节点 <code>5。</code>因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>说明:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>所有节点的值都是唯一的。</li>
|
||||
<li>p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉树中。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意:本题与主站 236 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
<p>输入一棵二叉树的根节点,求该树的深度。从根节点到叶节点依次经过的节点(含根、叶节点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>例如:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给定二叉树 <code>[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]</code>,</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre> 3
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
9 20
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
15 7</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回它的最大深度 3 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li><code>节点总数 <= 10000</code></li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意:本题与主站 104 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
<p>请完成一个函数,输入一个二叉树,该函数输出它的镜像。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>例如输入:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code> 4<br>
|
||||
/ \<br>
|
||||
2 7<br>
|
||||
/ \ / \<br>
|
||||
1 3 6 9</code><br>
|
||||
镜像输出:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code> 4<br>
|
||||
/ \<br>
|
||||
7 2<br>
|
||||
/ \ / \<br>
|
||||
9 6 3 1</code></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>限制:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code>0 <= 节点个数 <= 1000</code></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意:本题与主站 226 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/invert-binary-tree/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/invert-binary-tree/</a></p>
|
||||
50
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二维子矩阵的和 [O4NDxx].html
Normal file
50
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二维子矩阵的和 [O4NDxx].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
<p><big><small>给定一个二维矩阵 <code>matrix</code>,</small></big>以下类型的多个请求:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><big><small>计算其子矩形范围内元素的总和,该子矩阵的左上角为 <code>(row1, col1)</code> ,右下角为 <code>(row2, col2)</code> 。</small></big></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>实现 <code>NumMatrix</code> 类:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>NumMatrix(int[][] matrix)</code> 给定整数矩阵 <code>matrix</code> 进行初始化</li>
|
||||
<li><code>int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2)</code> 返回<big><small>左上角</small></big><big><small> <code>(row1, col1)</code> 、右下角 <code>(row2, col2)</code></small></big> 的子矩阵的元素总和。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img src="https://pic.leetcode-cn.com/1626332422-wUpUHT-image.png" style="width: 200px;" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>
|
||||
["NumMatrix","sumRegion","sumRegion","sumRegion"]
|
||||
[[[[3,0,1,4,2],[5,6,3,2,1],[1,2,0,1,5],[4,1,0,1,7],[1,0,3,0,5]]],[2,1,4,3],[1,1,2,2],[1,2,2,4]]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>
|
||||
[null, 8, 11, 12]
|
||||
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
NumMatrix numMatrix = new NumMatrix([[3,0,1,4,2],[5,6,3,2,1],[1,2,0,1,5],[4,1,0,1,7],[1,0,3,0,5]]]);
|
||||
numMatrix.sumRegion(2, 1, 4, 3); // return 8 (红色矩形框的元素总和)
|
||||
numMatrix.sumRegion(1, 1, 2, 2); // return 11 (绿色矩形框的元素总和)
|
||||
numMatrix.sumRegion(1, 2, 2, 4); // return 12 (蓝色矩形框的元素总和)
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>m == matrix.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>n == matrix[i].length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= m, n <= 200</code><meta charset="UTF-8" /></li>
|
||||
<li><code>-10<sup>5</sup> <= matrix[i][j] <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= row1 <= row2 < m</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= col1 <= col2 < n</code></li>
|
||||
<li><meta charset="UTF-8" />最多调用 <code>10<sup>4</sup></code> 次 <code>sumRegion</code> 方法</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 304 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/range-sum-query-2d-immutable/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/range-sum-query-2d-immutable/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
<p>在一个 n * m 的二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个高效的函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>现有矩阵 matrix 如下:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
[
|
||||
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
|
||||
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
|
||||
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
|
||||
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
|
||||
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
|
||||
]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给定 target = <code>5</code>,返回 <code>true</code>。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给定 target = <code>20</code>,返回 <code>false</code>。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>限制:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code>0 <= n <= 1000</code></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code>0 <= m <= 1000</code></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>注意:</strong>本题与主站 240 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix-ii/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix-ii/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
<p>编写一个函数,输入是一个无符号整数(以二进制串的形式),返回其二进制表达式中数字位数为 '1' 的个数(也被称为 <a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hamming_weight" target="_blank">汉明重量</a>).)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>请注意,在某些语言(如 Java)中,没有无符号整数类型。在这种情况下,输入和输出都将被指定为有符号整数类型,并且不应影响您的实现,因为无论整数是有符号的还是无符号的,其内部的二进制表示形式都是相同的。</li>
|
||||
<li>在 Java 中,编译器使用 <a href="https://baike.baidu.com/item/二进制补码/5295284">二进制补码</a> 记法来表示有符号整数。因此,在上面的 <strong>示例 3 </strong>中,输入表示有符号整数 <code>-3</code>。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>n = 11 (控制台输入 00000000000000000000000000001011)
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>3
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>输入的二进制串 <code><strong>00000000000000000000000000001011</strong> 中,共有三位为 '1'。</code>
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>n = 128 (控制台输入 00000000000000000000000010000000)
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>1
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>输入的二进制串 <strong>00000000000000000000000010000000</strong> 中,共有一位为 '1'。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>n = 4294967293 (控制台输入 11111111111111111111111111111101,部分语言中 n = -3)
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>31
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>输入的二进制串 <strong>11111111111111111111111111111101</strong> 中,共有 31 位为 '1'。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>输入必须是长度为 <code>32</code> 的 <strong>二进制串</strong> 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意:本题与主站 191 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-1-bits/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-1-bits/</a></p>
|
||||
31
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二进制加法 [JFETK5].html
Normal file
31
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/二进制加法 [JFETK5].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<p>给定两个 01 字符串 <code>a</code> 和 <code>b</code> ,请计算它们的和,并以二进制字符串的形式输出。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>输入为 <strong>非空 </strong>字符串且只包含数字 <code>1</code> 和 <code>0</code>。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> a = "11", b = "10"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> "101"</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> a = "1010", b = "1011"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> "10101"</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>每个字符串仅由字符 <code>'0'</code> 或 <code>'1'</code> 组成。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= a.length, b.length <= 10^4</code></li>
|
||||
<li>字符串如果不是 <code>"0"</code> ,就都不含前导零。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 67 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-binary/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-binary/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
<p>二进制数转字符串。给定一个介于0和1之间的实数(如0.72),类型为double,打印它的二进制表达式。如果该数字无法精确地用32位以内的二进制表示,则打印“ERROR”。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong> 输入</strong>:0.625
|
||||
<strong> 输出</strong>:"0.101"
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong> 输入</strong>:0.1
|
||||
<strong> 输出</strong>:"ERROR"
|
||||
<strong> 提示</strong>:0.1无法被二进制准确表示
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li>32位包括输出中的"0."这两位。</li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
41
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/井字游戏 [tic-tac-toe-lcci].html
Normal file
41
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/井字游戏 [tic-tac-toe-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
<p>设计一个算法,判断玩家是否赢了井字游戏。输入是一个 N x N 的数组棋盘,由字符" ","X"和"O"组成,其中字符" "代表一个空位。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>以下是井字游戏的规则:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>玩家轮流将字符放入空位(" ")中。</li>
|
||||
<li>第一个玩家总是放字符"O",且第二个玩家总是放字符"X"。</li>
|
||||
<li>"X"和"O"只允许放置在空位中,不允许对已放有字符的位置进行填充。</li>
|
||||
<li>当有N个相同(且非空)的字符填充任何行、列或对角线时,游戏结束,对应该字符的玩家获胜。</li>
|
||||
<li>当所有位置非空时,也算为游戏结束。</li>
|
||||
<li>如果游戏结束,玩家不允许再放置字符。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>如果游戏存在获胜者,就返回该游戏的获胜者使用的字符("X"或"O");如果游戏以平局结束,则返回 "Draw";如果仍会有行动(游戏未结束),则返回 "Pending"。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> board = ["O X"," XO","X O"]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> "X"
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> board = ["OOX","XXO","OXO"]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> "Draw"
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong> 没有玩家获胜且不存在空位
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> board = ["OOX","XXO","OX "]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> "Pending"
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong> 没有玩家获胜且仍存在空位
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= board.length == board[i].length <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li>输入一定遵循井字棋规则</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
20
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/交换和 [sum-swap-lcci].html
Normal file
20
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/交换和 [sum-swap-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
<p>给定两个整数数组,请交换一对数值(每个数组中取一个数值),使得两个数组所有元素的和相等。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回一个数组,第一个元素是第一个数组中要交换的元素,第二个元素是第二个数组中要交换的元素。若有多个答案,返回任意一个均可。若无满足条件的数值,返回空数组。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> array1 = [4, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2], array2 = [3, 6, 3, 3]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> [1, 3]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> array1 = <code>[1, 2, 3], array2 = [4, 5, 6]</code>
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[]</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= array1.length, array2.length <= 100000</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
15
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/交换数字 [swap-numbers-lcci].html
Normal file
15
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/交换数字 [swap-numbers-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<p>编写一个函数,不用临时变量,直接交换<code>numbers = [a, b]</code>中<code>a</code>与<code>b</code>的值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong> numbers = [1,2]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> [2,1]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>numbers.length == 2</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>-2147483647 <= numbers[i] <= 2147483647</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
38
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/交点 [intersection-lcci].html
Normal file
38
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/交点 [intersection-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
<p>给定两条线段(表示为起点<code>start = {X1, Y1}</code>和终点<code>end = {X2, Y2}</code>),如果它们有交点,请计算其交点,没有交点则返回空值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>要求浮点型误差不超过<code>10^-6</code>。若有多个交点(线段重叠)则返回 X 值最小的点,X 坐标相同则返回 Y 值最小的点。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>
|
||||
line1 = {0, 0}, {1, 0}
|
||||
line2 = {1, 1}, {0, -1}
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> {0.5, 0}
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>
|
||||
line1 = {0, 0}, {3, 3}
|
||||
line2 = {1, 1}, {2, 2}
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> {1, 1}
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>
|
||||
line1 = {0, 0}, {1, 1}
|
||||
line2 = {1, 0}, {2, 1}
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong> {},两条线段没有交点
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>坐标绝对值不会超过 2^7</li>
|
||||
<li>输入的坐标均是有效的二维坐标</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
<p>从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层的节点按从左到右的顺序打印,每一层打印到一行。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>例如:<br>
|
||||
给定二叉树: <code>[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]</code>,</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre> 3
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
9 20
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
15 7
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回其层次遍历结果:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>[
|
||||
[3],
|
||||
[9,20],
|
||||
[15,7]
|
||||
]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li><code>节点总数 <= 1000</code></li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意:本题与主站 102 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
<p>请实现一个函数按照之字形顺序打印二叉树,即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右到左的顺序打印,第三行再按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>例如:<br>
|
||||
给定二叉树: <code>[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]</code>,</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre> 3
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
9 20
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
15 7
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回其层次遍历结果:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>[
|
||||
[3],
|
||||
[20,9],
|
||||
[15,7]
|
||||
]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li><code>节点总数 <= 1000</code></li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
<p>从上到下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同一层的节点按照从左到右的顺序打印。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>例如:<br>
|
||||
给定二叉树: <code>[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]</code>,</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre> 3
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
9 20
|
||||
/ \
|
||||
15 7
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>[3,9,20,15,7]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li><code>节点总数 <= 1000</code></li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一棵 <strong>二叉树</strong> 的根节点 <code>root</code> ,这棵二叉树总共有 <code>n</code> 个节点。每个节点的值为 <code>1</code> 到 <code>n</code> 中的一个整数,且互不相同。给你一个整数 <code>startValue</code> ,表示起点节点 <code>s</code> 的值,和另一个不同的整数 <code>destValue</code> ,表示终点节点 <code>t</code> 的值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请找到从节点 <code>s</code> 到节点 <code>t</code> 的 <strong>最短路径</strong> ,并以字符串的形式返回每一步的方向。每一步用 <strong>大写</strong> 字母 <code>'L'</code> ,<code>'R'</code> 和 <code>'U'</code> 分别表示一种方向:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>'L'</code> 表示从一个节点前往它的 <strong>左孩子</strong> 节点。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>'R'</code> 表示从一个节点前往它的 <strong>右孩子</strong> 节点。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>'U'</code> 表示从一个节点前往它的 <strong>父</strong> 节点。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请你返回从 <code>s</code> 到 <code>t</code> <strong>最短路径</strong> 每一步的方向。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/11/15/eg1.png" style="width: 214px; height: 163px;"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>root = [5,1,2,3,null,6,4], startValue = 3, destValue = 6
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>"UURL"
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>最短路径为:3 → 1 → 5 → 2 → 6 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/11/15/eg2.png" style="width: 74px; height: 102px;"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>root = [2,1], startValue = 2, destValue = 1
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>"L"
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>最短路径为:2 → 1 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>树中节点数目为 <code>n</code> 。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>2 <= n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= Node.val <= n</code></li>
|
||||
<li>树中所有节点的值 <strong>互不相同</strong> 。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= startValue, destValue <= n</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>startValue != destValue</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
<p>一个整数数组 <code>original</code> 可以转变成一个 <strong>双倍</strong> 数组 <code>changed</code> ,转变方式为将 <code>original</code> 中每个元素 <strong>值乘以 2 </strong>加入数组中,然后将所有元素 <strong>随机打乱</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给你一个数组 <code>changed</code> ,如果 <code>change</code> 是 <strong>双倍</strong> 数组,那么请你返回 <code>original</code>数组,否则请返回空数组。<code>original</code> 的元素可以以 <strong>任意</strong> 顺序返回。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>changed = [1,3,4,2,6,8]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>[1,3,4]
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>一个可能的 original 数组为 [1,3,4] :
|
||||
- 将 1 乘以 2 ,得到 1 * 2 = 2 。
|
||||
- 将 3 乘以 2 ,得到 3 * 2 = 6 。
|
||||
- 将 4 乘以 2 ,得到 4 * 2 = 8 。
|
||||
其他可能的原数组方案为 [4,3,1] 或者 [3,1,4] 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>changed = [6,3,0,1]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>[]
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>changed 不是一个双倍数组。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>changed = [1]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>[]
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>changed 不是一个双倍数组。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= changed.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= changed[i] <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
<p>存在一个未知数组需要你进行还原,给你一个整数 <code>n</code> 表示该数组的长度。另给你一个数组 <code>sums</code> ,由未知数组中全部 <code>2<sup>n</sup></code> 个 <strong>子集的和</strong> 组成(子集中的元素没有特定的顺序)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回一个长度为 <code>n</code> 的数组<em> </em><code>ans</code><em> </em>表示还原得到的未知数组。如果存在 <strong>多种</strong> 答案,只需返回其中 <strong>任意一个</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>如果可以由数组 <code>arr</code> 删除部分元素(也可能不删除或全删除)得到数组 <code>sub</code> ,那么数组 <code>sub</code> 就是数组 <code>arr</code> 的一个<strong> 子集</strong> 。<code>sub</code> 的元素之和就是 <code>arr</code> 的一个 <strong>子集的和</strong> 。一个空数组的元素之和为 <code>0</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>注意:</strong>生成的测试用例将保证至少存在一个正确答案。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>n = 3, sums = [-3,-2,-1,0,0,1,2,3]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>[1,2,-3]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>[1,2,-3] 能够满足给出的子集的和:
|
||||
- []:和是 0
|
||||
- [1]:和是 1
|
||||
- [2]:和是 2
|
||||
- [1,2]:和是 3
|
||||
- [-3]:和是 -3
|
||||
- [1,-3]:和是 -2
|
||||
- [2,-3]:和是 -1
|
||||
- [1,2,-3]:和是 0
|
||||
注意,[1,2,-3] 的任何排列和 [-1,-2,3] 的任何排列都会被视作正确答案。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>n = 2, sums = [0,0,0,0]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>[0,0]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>唯一的正确答案是 [0,0] 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>n = 4, sums = [0,0,5,5,4,-1,4,9,9,-1,4,3,4,8,3,8]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>[0,-1,4,5]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>[0,-1,4,5] 能够满足给出的子集的和。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n <= 15</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>sums.length == 2<sup>n</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>-10<sup>4</sup> <= sums[i] <= 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
<p>输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,3,2]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>[2,3,1]</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>限制:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code>0 <= 链表长度 <= 10000</code></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的字符串 <code>street</code> 。<code>street</code> 中每个字符要么是表示房屋的 <code>'H'</code> ,要么是表示空位的 <code>'.'</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>你可以在 <strong>空位</strong> 放置水桶,从相邻的房屋收集雨水。位置在 <code>i - 1</code> <strong>或者</strong> <code>i + 1</code> 的水桶可以收集位置为 <code>i</code> 处房屋的雨水。一个水桶如果相邻两个位置都有房屋,那么它可以收集 <strong>两个</strong> 房屋的雨水。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在确保 <strong>每个</strong> 房屋旁边都 <strong>至少</strong> 有一个水桶的前提下,请你返回需要的 <strong>最少</strong> 水桶数。如果无解请返回 <code>-1</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>street = "H..H"
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>2
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
我们可以在下标为 1 和 2 处放水桶。
|
||||
"H..H" -> "HBBH"('B' 表示放置水桶)。
|
||||
下标为 0 处的房屋右边有水桶,下标为 3 处的房屋左边有水桶。
|
||||
所以每个房屋旁边都至少有一个水桶收集雨水。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>street = ".H.H."
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>1
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
我们可以在下标为 2 处放置一个水桶。
|
||||
".H.H." -> ".HBH."('B' 表示放置水桶)。
|
||||
下标为 1 处的房屋右边有水桶,下标为 3 处的房屋左边有水桶。
|
||||
所以每个房屋旁边都至少有一个水桶收集雨水。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>street = ".HHH."
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>-1
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
没有空位可以放置水桶收集下标为 2 处的雨水。
|
||||
所以没有办法收集所有房屋的雨水。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 4:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>street = "H"
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>-1
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
没有空位放置水桶。
|
||||
所以没有办法收集所有房屋的雨水。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 5:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>street = "."
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>0
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
没有房屋需要收集雨水。
|
||||
所以需要 0 个水桶。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= street.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>street[i]</code> 要么是 <code>'H'</code> ,要么是 <code>'.'</code> 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的数组 <code>nums</code> ,数组由若干 <strong>互不相同</strong> 的整数组成。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code>nums</code> 中有一个值最小的元素和一个值最大的元素。分别称为 <strong>最小值</strong> 和 <strong>最大值</strong> 。你的目标是从数组中移除这两个元素。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>一次 <strong>删除</strong> 操作定义为从数组的 <strong>前面</strong> 移除一个元素或从数组的 <strong>后面</strong> 移除一个元素。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回将数组中最小值和最大值 <strong>都</strong> 移除需要的最小删除次数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>nums = [2,<em><strong>10</strong></em>,7,5,4,<em><strong>1</strong></em>,8,6]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>5
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
数组中的最小元素是 nums[5] ,值为 1 。
|
||||
数组中的最大元素是 nums[1] ,值为 10 。
|
||||
将最大值和最小值都移除需要从数组前面移除 2 个元素,从数组后面移除 3 个元素。
|
||||
结果是 2 + 3 = 5 ,这是所有可能情况中的最小删除次数。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>nums = [0,<em><strong>-4</strong></em>,<em><strong>19</strong></em>,1,8,-2,-3,5]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>3
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
数组中的最小元素是 nums[1] ,值为 -4 。
|
||||
数组中的最大元素是 nums[2] ,值为 19 。
|
||||
将最大值和最小值都移除需要从数组前面移除 3 个元素。
|
||||
结果是 3 ,这是所有可能情况中的最小删除次数。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>nums = [<em><strong>101</strong></em>]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>1
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
数组中只有这一个元素,那么它既是数组中的最小值又是数组中的最大值。
|
||||
移除它只需要 1 次删除操作。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>-10<sup>5</sup> <= nums[i] <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>nums</code> 中的整数 <strong>互不相同</strong></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
53
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/从根节点到叶节点的路径数字之和 [3Etpl5].html
Normal file
53
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/从根节点到叶节点的路径数字之和 [3Etpl5].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个二叉树的根节点 <code>root</code> ,树中每个节点都存放有一个 <code>0</code> 到 <code>9</code> 之间的数字。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="original__bRMd">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<p>每条从根节点到叶节点的路径都代表一个数字:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>例如,从根节点到叶节点的路径 <code>1 -> 2 -> 3</code> 表示数字 <code>123</code> 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>计算从根节点到叶节点生成的 <strong>所有数字之和</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>叶节点</strong> 是指没有子节点的节点。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/02/19/num1tree.jpg" style="width: 212px; height: 182px;" />
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>root = [1,2,3]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>25
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
从根到叶子节点路径 <code>1->2</code> 代表数字 <code>12</code>
|
||||
从根到叶子节点路径 <code>1->3</code> 代表数字 <code>13</code>
|
||||
因此,数字总和 = 12 + 13 = <code>25</code></pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/02/19/num2tree.jpg" style="width: 292px; height: 302px;" />
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>root = [4,9,0,5,1]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>1026
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
从根到叶子节点路径 <code>4->9->5</code> 代表数字 495
|
||||
从根到叶子节点路径 <code>4->9->1</code> 代表数字 491
|
||||
从根到叶子节点路径 <code>4->0</code> 代表数字 40
|
||||
因此,数字总和 = 495 + 491 + 40 = <code>1026</code>
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>树中节点的数目在范围 <code>[1, 1000]</code> 内</li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= Node.val <= 9</code></li>
|
||||
<li>树的深度不超过 <code>10</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 129 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
<p>你有 <code>n</code> 道不同菜的信息。给你一个字符串数组 <code>recipes</code> 和一个二维字符串数组 <code>ingredients</code> 。第 <code>i</code> 道菜的名字为 <code>recipes[i]</code> ,如果你有它 <strong>所有</strong> 的原材料 <code>ingredients[i]</code> ,那么你可以 <strong>做出</strong> 这道菜。一道菜的原材料可能是 <strong>另一道</strong> 菜,也就是说 <code>ingredients[i]</code> 可能包含 <code>recipes</code> 中另一个字符串。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>同时给你一个字符串数组 <code>supplies</code> ,它包含你初始时拥有的所有原材料,每一种原材料你都有无限多。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请你返回你可以做出的所有菜。你可以以 <strong>任意顺序</strong> 返回它们。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>注意两道菜在它们的原材料中可能互相包含。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>recipes = ["bread"], ingredients = [["yeast","flour"]], supplies = ["yeast","flour","corn"]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>["bread"]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
我们可以做出 "bread" ,因为我们有原材料 "yeast" 和 "flour" 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>recipes = ["bread","sandwich"], ingredients = [["yeast","flour"],["bread","meat"]], supplies = ["yeast","flour","meat"]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>["bread","sandwich"]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
我们可以做出 "bread" ,因为我们有原材料 "yeast" 和 "flour" 。
|
||||
我们可以做出 "sandwich" ,因为我们有原材料 "meat" 且可以做出原材料 "bread" 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>recipes = ["bread","sandwich","burger"], ingredients = [["yeast","flour"],["bread","meat"],["sandwich","meat","bread"]], supplies = ["yeast","flour","meat"]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>["bread","sandwich","burger"]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
我们可以做出 "bread" ,因为我们有原材料 "yeast" 和 "flour" 。
|
||||
我们可以做出 "sandwich" ,因为我们有原材料 "meat" 且可以做出原材料 "bread" 。
|
||||
我们可以做出 "burger" ,因为我们有原材料 "meat" 且可以做出原材料 "bread" 和 "sandwich" 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 4:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>recipes = ["bread"], ingredients = [["yeast","flour"]], supplies = ["yeast"]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>[]
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
我们没法做出任何菜,因为我们只有原材料 "yeast" 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>n == recipes.length == ingredients.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= ingredients[i].length, supplies.length <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= recipes[i].length, ingredients[i][j].length, supplies[k].length <= 10</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>recipes[i], ingredients[i][j]</code> 和 <code>supplies[k]</code> 只包含小写英文字母。</li>
|
||||
<li>所有 <code>recipes</code> 和 <code>supplies</code> 中的值互不相同。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>ingredients[i]</code> 中的字符串互不相同。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的二维整数数组 <code>grid</code> ,它的大小为 <code>m x n</code> ,表示一个商店中物品的分布图。数组中的整数含义为:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>0</code> 表示无法穿越的一堵墙。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>1</code> 表示可以自由通过的一个空格子。</li>
|
||||
<li>所有其他正整数表示该格子内的一样物品的价格。你可以自由经过这些格子。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>从一个格子走到上下左右相邻格子花费 <code>1</code> 步。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>同时给你一个整数数组 <code>pricing</code> 和 <code>start</code> ,其中 <code>pricing = [low, high]</code> 且 <code>start = [row, col]</code> ,表示你开始位置为 <code>(row, col)</code> ,同时你只对物品价格在<strong> 闭区间</strong> <code>[low, high]</code> 之内的物品感兴趣。同时给你一个整数 <code>k</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>你想知道给定范围 <strong>内</strong> 且 <strong>排名最高</strong> 的 <code>k</code> 件物品的 <strong>位置</strong> 。排名按照优先级从高到低的以下规则制定:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li>距离:定义为从 <code>start</code> 到一件物品的最短路径需要的步数(<strong>较近</strong> 距离的排名更高)。</li>
|
||||
<li>价格:<strong>较低</strong> 价格的物品有更高优先级,但只考虑在给定范围之内的价格。</li>
|
||||
<li>行坐标:<strong>较小</strong> 行坐标的有更高优先级。</li>
|
||||
<li>列坐标:<strong>较小</strong> 列坐标的有更高优先级。</li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请你返回给定价格内排名最高的 <code>k</code> 件物品的坐标,将它们按照排名排序后返回。如果给定价格内少于 <code>k</code> 件物品,那么请将它们的坐标 <strong>全部</strong> 返回。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/12/16/example1drawio.png" style="width: 200px; height: 151px;"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>grid = [[1,2,0,1],[1,3,0,1],[0,2,5,1]], pricing = [2,5], start = [0,0], k = 3
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>[[0,1],[1,1],[2,1]]
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>起点为 (0,0) 。
|
||||
价格范围为 [2,5] ,我们可以选择的物品坐标为 (0,1),(1,1),(2,1) 和 (2,2) 。
|
||||
这些物品的排名为:
|
||||
- (0,1) 距离为 1
|
||||
- (1,1) 距离为 2
|
||||
- (2,1) 距离为 3
|
||||
- (2,2) 距离为 4
|
||||
所以,给定价格范围内排名最高的 3 件物品的坐标为 (0,1),(1,1) 和 (2,1) 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/12/16/example2drawio1.png" style="width: 200px; height: 151px;"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>grid = [[1,2,0,1],[1,3,3,1],[0,2,5,1]], pricing = [2,3], start = [2,3], k = 2
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>[[2,1],[1,2]]
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>起点为 (2,3) 。
|
||||
价格范围为 [2,3] ,我们可以选择的物品坐标为 (0,1),(1,1),(1,2) 和 (2,1) 。
|
||||
这些物品的排名为:
|
||||
- (2,1) 距离为 2 ,价格为 2
|
||||
- (1,2) 距离为 2 ,价格为 3
|
||||
- (1,1) 距离为 3
|
||||
- (0,1) 距离为 4
|
||||
所以,给定价格范围内排名最高的 2 件物品的坐标为 (2,1) 和 (1,2) 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/12/30/example3.png" style="width: 149px; height: 150px;"></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>grid = [[1,1,1],[0,0,1],[2,3,4]], pricing = [2,3], start = [0,0], k = 3
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>[[2,1],[2,0]]
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>起点为 (0,0) 。
|
||||
价格范围为 [2,3] ,我们可以选择的物品坐标为 (2,0) 和 (2,1) 。
|
||||
这些物品的排名为:
|
||||
- (2,1) 距离为 5
|
||||
- (2,0) 距离为 6
|
||||
所以,给定价格范围内排名最高的 2 件物品的坐标为 (2,1) 和 (2,0) 。
|
||||
注意,k = 3 但给定价格范围内只有 2 件物品。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>m == grid.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>n == grid[i].length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= m, n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= m * n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= grid[i][j] <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>pricing.length == 2</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>2 <= low <= high <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>start.length == 2</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= row <= m - 1</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= col <= n - 1</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>grid[row][col] > 0</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= k <= m * n</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
38
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/传递信息 [chuan-di-xin-xi].html
Normal file
38
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/传递信息 [chuan-di-xin-xi].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
<p>小朋友 A 在和 ta 的小伙伴们玩传信息游戏,游戏规则如下:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ol>
|
||||
<li>有 n 名玩家,所有玩家编号分别为 0 ~ n-1,其中小朋友 A 的编号为 0</li>
|
||||
<li>每个玩家都有固定的若干个可传信息的其他玩家(也可能没有)。传信息的关系是单向的(比如 A 可以向 B 传信息,但 B 不能向 A 传信息)。</li>
|
||||
<li>每轮信息必须需要传递给另一个人,且信息可重复经过同一个人</li>
|
||||
</ol>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给定总玩家数 <code>n</code>,以及按 <code>[玩家编号,对应可传递玩家编号]</code> 关系组成的二维数组 <code>relation</code>。返回信息从小 A (编号 0 ) 经过 <code>k</code> 轮传递到编号为 n-1 的小伙伴处的方案数;若不能到达,返回 0。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>
|
||||
<p>输入:<code>n = 5, relation = [[0,2],[2,1],[3,4],[2,3],[1,4],[2,0],[0,4]], k = 3</code></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>输出:<code>3</code></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>解释:信息从小 A 编号 0 处开始,经 3 轮传递,到达编号 4。共有 3 种方案,分别是 0->2->0->4, 0->2->1->4, 0->2->3->4。</p>
|
||||
</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>
|
||||
<p>输入:<code>n = 3, relation = [[0,2],[2,1]], k = 2</code></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>输出:<code>0</code></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>解释:信息不能从小 A 处经过 2 轮传递到编号 2</p>
|
||||
</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>限制:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>2 <= n <= 10</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= k <= 5</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= relation.length <= 90, 且 relation[i].length == 2</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= relation[i][0],relation[i][1] < n 且 relation[i][0] != relation[i][1]</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个字符串数组 <code>patterns</code> 和一个字符串 <code>word</code> ,统计 <code>patterns</code> 中有多少个字符串是 <code>word</code> 的子字符串。返回字符串数目。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>子字符串</strong> 是字符串中的一个连续字符序列。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>patterns = ["a","abc","bc","d"], word = "abc"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>3
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
- "a" 是 "<em><strong>a</strong></em>bc" 的子字符串。
|
||||
- "abc" 是 "<em><strong>abc</strong></em>" 的子字符串。
|
||||
- "bc" 是 "a<em><strong>bc</strong></em>" 的子字符串。
|
||||
- "d" 不是 "abc" 的子字符串。
|
||||
patterns 中有 3 个字符串作为子字符串出现在 word 中。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>patterns = ["a","b","c"], word = "aaaaabbbbb"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>2
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
- "a" 是 "a<em><strong>a</strong></em>aaabbbbb" 的子字符串。
|
||||
- "b" 是 "aaaaabbbb<em><strong>b</strong></em>" 的子字符串。
|
||||
- "c" 不是 "aaaaabbbbb" 的字符串。
|
||||
patterns 中有 2 个字符串作为子字符串出现在 word 中。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>patterns = ["a","a","a"], word = "ab"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>3
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>patterns 中的每个字符串都作为子字符串出现在 word "<em><strong>a</strong></em>b" 中。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= patterns.length <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= patterns[i].length <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= word.length <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>patterns[i]</code> 和 <code>word</code> 由小写英文字母组成</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
<p>给你 <code>n</code> 个任务和 <code>m</code> 个工人。每个任务需要一定的力量值才能完成,需要的力量值保存在下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的整数数组 <code>tasks</code> 中,第 <code>i</code> 个任务需要 <code>tasks[i]</code> 的力量才能完成。每个工人的力量值保存在下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的整数数组 <code>workers</code> 中,第 <code>j</code> 个工人的力量值为 <code>workers[j]</code> 。每个工人只能完成 <strong>一个</strong> 任务,且力量值需要 <strong>大于等于</strong> 该任务的力量要求值(即 <code>workers[j] >= tasks[i]</code> )。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>除此以外,你还有 <code>pills</code> 个神奇药丸,可以给 <strong>一个工人的力量值</strong> 增加 <code>strength</code> 。你可以决定给哪些工人使用药丸,但每个工人 <strong>最多</strong> 只能使用 <strong>一片</strong> 药丸。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给你下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的整数数组<code>tasks</code> 和 <code>workers</code> 以及两个整数 <code>pills</code> 和 <code>strength</code> ,请你返回 <strong>最多</strong> 有多少个任务可以被完成。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>tasks = [<em><strong>3</strong></em>,<em><strong>2</strong></em>,<em><strong>1</strong></em>], workers = [<em><strong>0</strong></em>,<em><strong>3</strong></em>,<em><strong>3</strong></em>], pills = 1, strength = 1
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>3
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
我们可以按照如下方案安排药丸:
|
||||
- 给 0 号工人药丸。
|
||||
- 0 号工人完成任务 2(0 + 1 >= 1)
|
||||
- 1 号工人完成任务 1(3 >= 2)
|
||||
- 2 号工人完成任务 0(3 >= 3)
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>tasks = [<em><strong>5</strong></em>,4], workers = [<em><strong>0</strong></em>,0,0], pills = 1, strength = 5
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>1
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
我们可以按照如下方案安排药丸:
|
||||
- 给 0 号工人药丸。
|
||||
- 0 号工人完成任务 0(0 + 5 >= 5)
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>tasks = [<em><strong>10</strong></em>,<em><strong>15</strong></em>,30], workers = [<em><strong>0</strong></em>,<em><strong>10</strong></em>,10,10,10], pills = 3, strength = 10
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>2
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
我们可以按照如下方案安排药丸:
|
||||
- 给 0 号和 1 号工人药丸。
|
||||
- 0 号工人完成任务 0(0 + 10 >= 10)
|
||||
- 1 号工人完成任务 1(10 + 10 >= 15)
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 4:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>tasks = [<em><strong>5</strong></em>,9,<em><strong>8</strong></em>,<em><strong>5</strong></em>,9], workers = [1,<em><strong>6</strong></em>,<em><strong>4</strong></em>,2,<em><strong>6</strong></em>], pills = 1, strength = 5
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>3
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
我们可以按照如下方案安排药丸:
|
||||
- 给 2 号工人药丸。
|
||||
- 1 号工人完成任务 0(6 >= 5)
|
||||
- 2 号工人完成任务 2(4 + 5 >= 8)
|
||||
- 4 号工人完成任务 3(6 >= 5)
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>n == tasks.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>m == workers.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n, m <= 5 * 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= pills <= m</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= tasks[i], workers[j], strength <= 10<sup>9</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
<p>给你 <code>n</code> 个项目,编号从 <code>0</code> 到 <code>n - 1</code> 。同时给你一个整数数组 <code>milestones</code> ,其中每个 <code>milestones[i]</code> 表示第 <code>i</code> 个项目中的阶段任务数量。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>你可以按下面两个规则参与项目中的工作:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>每周,你将会完成 <strong>某一个</strong> 项目中的 <strong>恰好一个</strong> 阶段任务。你每周都 <strong>必须</strong> 工作。</li>
|
||||
<li>在 <strong>连续的</strong> 两周中,你 <strong>不能</strong> 参与并完成同一个项目中的两个阶段任务。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>一旦所有项目中的全部阶段任务都完成,或者仅剩余一个阶段任务都会导致你违反上面的规则,那么你将 <strong>停止工作</strong> 。注意,由于这些条件的限制,你可能无法完成所有阶段任务。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回在不违反上面规则的情况下你 <strong>最多</strong> 能工作多少周。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>milestones = [1,2,3]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>6
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>一种可能的情形是:
|
||||
- 第 1 周,你参与并完成项目 0 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
- 第 2 周,你参与并完成项目 2 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
- 第 3 周,你参与并完成项目 1 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
- 第 4 周,你参与并完成项目 2 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
- 第 5 周,你参与并完成项目 1 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
- 第 6 周,你参与并完成项目 2 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
总周数是 6 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>milestones = [5,2,1]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>7
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>一种可能的情形是:
|
||||
- 第 1 周,你参与并完成项目 0 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
- 第 2 周,你参与并完成项目 1 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
- 第 3 周,你参与并完成项目 0 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
- 第 4 周,你参与并完成项目 1 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
- 第 5 周,你参与并完成项目 0 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
- 第 6 周,你参与并完成项目 2 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
- 第 7 周,你参与并完成项目 0 中的一个阶段任务。
|
||||
总周数是 7 。
|
||||
注意,你不能在第 8 周参与完成项目 0 中的最后一个阶段任务,因为这会违反规则。
|
||||
因此,项目 0 中会有一个阶段任务维持未完成状态。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>n == milestones.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= milestones[i] <= 10<sup>9</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个下标从 <strong>1</strong> 开始的二进制矩阵,其中 <code>0</code> 表示陆地,<code>1</code> 表示水域。同时给你 <code>row</code> 和 <code>col</code> 分别表示矩阵中行和列的数目。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>一开始在第 <code>0</code> 天,<strong>整个</strong> 矩阵都是 <strong>陆地</strong> 。但每一天都会有一块新陆地被 <strong>水</strong> 淹没变成水域。给你一个下标从 <strong>1</strong> 开始的二维数组 <code>cells</code> ,其中 <code>cells[i] = [r<sub>i</sub>, c<sub>i</sub>]</code> 表示在第 <code>i</code> 天,第 <code>r<sub>i</sub></code> 行 <code>c<sub>i</sub></code> 列(下标都是从 <strong>1</strong> 开始)的陆地会变成 <strong>水域</strong> (也就是 <code>0</code> 变成 <code>1</code> )。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>你想知道从矩阵最 <strong>上面</strong> 一行走到最 <strong>下面</strong> 一行,且只经过陆地格子的 <strong>最后一天</strong> 是哪一天。你可以从最上面一行的 <strong>任意</strong> 格子出发,到达最下面一行的 <strong>任意</strong> 格子。你只能沿着 <strong>四个</strong> 基本方向移动(也就是上下左右)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请返回只经过陆地格子能从最 <strong>上面</strong> 一行走到最 <strong>下面</strong> 一行的 <strong>最后一天</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/07/27/1.png" style="width: 624px; height: 162px;">
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>row = 2, col = 2, cells = [[1,1],[2,1],[1,2],[2,2]]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>2
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>上图描述了矩阵从第 0 天开始是如何变化的。
|
||||
可以从最上面一行到最下面一行的最后一天是第 2 天。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/07/27/2.png" style="width: 504px; height: 178px;">
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>row = 2, col = 2, cells = [[1,1],[1,2],[2,1],[2,2]]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>1
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>上图描述了矩阵从第 0 天开始是如何变化的。
|
||||
可以从最上面一行到最下面一行的最后一天是第 1 天。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/07/27/3.png" style="width: 666px; height: 167px;">
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>row = 3, col = 3, cells = [[1,2],[2,1],[3,3],[2,2],[1,1],[1,3],[2,3],[3,2],[3,1]]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>3
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>上图描述了矩阵从第 0 天开始是如何变化的。
|
||||
可以从最上面一行到最下面一行的最后一天是第 3 天。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>2 <= row, col <= 2 * 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>4 <= row * col <= 2 * 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>cells.length == row * col</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= r<sub>i</sub> <= row</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= c<sub>i</sub> <= col</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>cells</code> 中的所有格子坐标都是 <strong>唯一</strong> 的。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<p>给你两个字符串 <code>s</code> 和 <code>t</code> 。在一步操作中,你可以给 <code>s</code> 或者 <code>t</code> 追加 <strong>任一字符</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回使 <code>s</code> 和 <code>t</code> 互为 <strong>字母异位词</strong> 所需的最少步骤数<em>。</em></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>字母异位词 </strong>指字母相同但是顺序不同(或者相同)的字符串。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>s = "<em><strong>lee</strong>t</em>co<em><strong>de</strong></em>", t = "co<em><strong>a</strong></em>t<em><strong>s</strong></em>"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>7
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
- 执行 2 步操作,将 "as" 追加到 s = "leetcode" 中,得到 s = "leetcode<em><strong>as</strong></em>" 。
|
||||
- 执行 5 步操作,将 "leede" 追加到 t = "coats" 中,得到 t = "coats<em><strong>leede</strong></em>" 。
|
||||
"leetcodeas" 和 "coatsleede" 互为字母异位词。
|
||||
总共用去 2 + 5 = 7 步。
|
||||
可以证明,无法用少于 7 步操作使这两个字符串互为字母异位词。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>s = "night", t = "thing"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>0
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>给出的字符串已经互为字母异位词。因此,不需要任何进一步操作。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= s.length, t.length <= 2 * 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>s</code> 和 <code>t</code> 由小写英文字符组成</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个字符串 <code>s</code> ,<strong>下标从 0 开始</strong> ,且长度为偶数 <code>n</code> 。字符串 <strong>恰好</strong> 由 <code>n / 2</code> 个开括号 <code>'['</code> 和 <code>n / 2</code> 个闭括号 <code>']'</code> 组成。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>只有能满足下述所有条件的字符串才能称为 <strong>平衡字符串</strong> :</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>字符串是一个空字符串,或者</li>
|
||||
<li>字符串可以记作 <code>AB</code> ,其中 <code>A</code> 和 <code>B</code> 都是 <strong>平衡字符串</strong> ,或者</li>
|
||||
<li>字符串可以写成 <code>[C]</code> ,其中 <code>C</code> 是一个 <strong>平衡字符串</strong> 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>你可以交换 <strong>任意</strong> 两个下标所对应的括号 <strong>任意</strong> 次数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回使<em> </em><code>s</code> 变成 <strong>平衡字符串</strong> 所需要的 <strong>最小</strong> 交换次数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>s = "][]["
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>1
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>交换下标 0 和下标 3 对应的括号,可以使字符串变成平衡字符串。
|
||||
最终字符串变成 "[[]]" 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>s = "]]][[["
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>2
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>执行下述操作可以使字符串变成平衡字符串:
|
||||
- 交换下标 0 和下标 4 对应的括号,s = "[]][][" 。
|
||||
- 交换下标 1 和下标 5 对应的括号,s = "[[][]]" 。
|
||||
最终字符串变成 "[[][]]" 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>s = "[]"
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>0
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>这个字符串已经是平衡字符串。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>n == s.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>2 <= n <= 10<sup>6</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>n</code> 为偶数</li>
|
||||
<li><code>s[i]</code> 为<code>'['</code> 或 <code>']'</code></li>
|
||||
<li>开括号 <code>'['</code> 的数目为 <code>n / 2</code> ,闭括号 <code>']'</code> 的数目也是 <code>n / 2</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始包含 <code>n</code> 个正整数的数组 <code>arr</code> ,和一个正整数 <code>k</code> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>如果对于每个满足 <code>k <= i <= n-1</code> 的下标 <code>i</code> ,都有 <code>arr[i-k] <= arr[i]</code> ,那么我们称 <code>arr</code> 是 <strong>K</strong> <strong>递增</strong> 的。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>比方说,<code>arr = [4, 1, 5, 2, 6, 2]</code> 对于 <code>k = 2</code> 是 K 递增的,因为:
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>arr[0] <= arr[2] (4 <= 5)</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>arr[1] <= arr[3] (1 <= 2)</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>arr[2] <= arr[4] (5 <= 6)</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>arr[3] <= arr[5] (2 <= 2)</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>但是,相同的数组 <code>arr</code> 对于 <code>k = 1</code> 不是 K 递增的(因为 <code>arr[0] > arr[1]</code>),对于 <code>k = 3</code> 也不是 K 递增的(因为 <code>arr[0] > arr[3]</code> )。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>每一次 <strong>操作</strong> 中,你可以选择一个下标 <code>i</code> 并将 <code>arr[i]</code> <strong>改成任意 </strong>正整数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请你返回对于给定的 <code>k</code> ,使数组变成 K 递增的 <strong>最少操作次数</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>arr = [5,4,3,2,1], k = 1
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>4
|
||||
<strong>解释:
|
||||
</strong>对于 k = 1 ,数组最终必须变成非递减的。
|
||||
可行的 K 递增结果数组为 [5,<em><strong>6</strong></em>,<em><strong>7</strong></em>,<em><strong>8</strong></em>,<em><strong>9</strong></em>],[<em><strong>1</strong></em>,<em><strong>1</strong></em>,<em><strong>1</strong></em>,<em><strong>1</strong></em>,1],[<em><strong>2</strong></em>,<em><strong>2</strong></em>,3,<em><strong>4</strong></em>,<em><strong>4</strong></em>] 。它们都需要 4 次操作。
|
||||
次优解是将数组变成比方说 [<em><strong>6</strong></em>,<em><strong>7</strong></em>,<em><strong>8</strong></em>,<em><strong>9</strong></em>,<em><strong>10</strong></em>] ,因为需要 5 次操作。
|
||||
显然我们无法使用少于 4 次操作将数组变成 K 递增的。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>arr = [4,1,5,2,6,2], k = 2
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>0
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
这是题目描述中的例子。
|
||||
对于每个满足 2 <= i <= 5 的下标 i ,有 arr[i-2] <=<b> </b>arr[i] 。
|
||||
由于给定数组已经是 K 递增的,我们不需要进行任何操作。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>arr = [4,1,5,2,6,2], k = 3
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>2
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
下标 3 和 5 是仅有的 3 <= i <= 5 且不满足 arr[i-3] <= arr[i] 的下标。
|
||||
将数组变成 K 递增的方法之一是将 arr[3] 变为 4 ,且将 arr[5] 变成 5 。
|
||||
数组变为 [4,1,5,<em><strong>4</strong></em>,6,<em><strong>5</strong></em>] 。
|
||||
可能有其他方法将数组变为 K 递增的,但没有任何一种方法需要的操作次数小于 2 次。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= arr.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= arr[i], k <= arr.length</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的数组 <code>nums</code> ,该数组由 <code>n</code> 个正整数组成。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>如果满足下述条件,则数组 <code>nums</code> 是一个 <strong>交替数组</strong> :</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>nums[i - 2] == nums[i]</code> ,其中 <code>2 <= i <= n - 1</code> 。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>nums[i - 1] != nums[i]</code> ,其中 <code>1 <= i <= n - 1</code> 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在一步 <strong>操作</strong> 中,你可以选择下标 <code>i</code> 并将 <code>nums[i]</code> <strong>更改</strong> 为 <strong>任一</strong> 正整数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回使数组变成交替数组的 <strong>最少操作数</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>nums = [3,1,3,2,4,3]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>3
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
使数组变成交替数组的方法之一是将该数组转换为 [3,1,3,<em><strong>1</strong></em>,<em><strong>3</strong></em>,<em><strong>1</strong></em>] 。
|
||||
在这种情况下,操作数为 3 。
|
||||
可以证明,操作数少于 3 的情况下,无法使数组变成交替数组。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>nums = [1,2,2,2,2]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>2
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
使数组变成交替数组的方法之一是将该数组转换为 [1,2,<em><strong>1</strong></em>,2,<em><strong>1</strong></em>].
|
||||
在这种情况下,操作数为 2 。
|
||||
注意,数组不能转换成 [<em><strong>2</strong></em>,2,2,2,2] 。因为在这种情况下,nums[0] == nums[1],不满足交替数组的条件。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums[i] <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个整数数组 <code>nums</code> 。每一次操作中,你可以将 <code>nums</code> 中 <strong>任意</strong> 一个元素替换成 <strong>任意 </strong>整数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>如果 <code>nums</code> 满足以下条件,那么它是 <strong>连续的</strong> :</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>nums</code> 中所有元素都是 <b>互不相同</b> 的。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>nums</code> 中 <strong>最大</strong> 元素与 <strong>最小</strong> 元素的差等于 <code>nums.length - 1</code> 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>比方说,<code>nums = [4, 2, 5, 3]</code> 是 <strong>连续的</strong> ,但是 <code>nums = [1, 2, 3, 5, 6]</code> <strong>不是连续的</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请你返回使 <code>nums</code> <strong>连续</strong> 的 <strong>最少</strong> 操作次数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>nums = [4,2,5,3]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>0
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>nums 已经是连续的了。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>nums = [1,2,3,5,6]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>1
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>一个可能的解是将最后一个元素变为 4 。
|
||||
结果数组为 [1,2,3,5,4] ,是连续数组。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>nums = [1,10,100,1000]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>3
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>一个可能的解是:
|
||||
- 将第二个元素变为 2 。
|
||||
- 将第三个元素变为 3 。
|
||||
- 将第四个元素变为 4 。
|
||||
结果数组为 [1,2,3,4] ,是连续数组。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums[i] <= 10<sup>9</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
<p>一个房间里有 <code>n</code> 个座位和 <code>n</code> 名学生,房间用一个数轴表示。给你一个长度为 <code>n</code> 的数组 <code>seats</code> ,其中 <code>seats[i]</code> 是第 <code>i</code> 个座位的位置。同时给你一个长度为 <code>n</code> 的数组 <code>students</code> ,其中 <code>students[j]</code> 是第 <code>j</code> 位学生的位置。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>你可以执行以下操作任意次:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>增加或者减少第 <code>i</code> 位学生的位置,每次变化量为 <code>1</code> (也就是将第 <code>i</code> 位学生从位置 <code>x</code> 移动到 <code>x + 1</code> 或者 <code>x - 1</code>)</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请你返回使所有学生都有座位坐的 <strong>最少移动次数</strong> ,并确保没有两位学生的座位相同。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>请注意,初始时有可能有多个座位或者多位学生在 <strong>同一</strong> 位置。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>seats = [3,1,5], students = [2,7,4]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>4
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>学生移动方式如下:
|
||||
- 第一位学生从位置 2 移动到位置 1 ,移动 1 次。
|
||||
- 第二位学生从位置 7 移动到位置 5 ,移动 2 次。
|
||||
- 第三位学生从位置 4 移动到位置 3 ,移动 1 次。
|
||||
总共 1 + 2 + 1 = 4 次移动。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>seats = [4,1,5,9], students = [1,3,2,6]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>7
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>学生移动方式如下:
|
||||
- 第一位学生不移动。
|
||||
- 第二位学生从位置 3 移动到位置 4 ,移动 1 次。
|
||||
- 第三位学生从位置 2 移动到位置 5 ,移动 3 次。
|
||||
- 第四位学生从位置 6 移动到位置 9 ,移动 3 次。
|
||||
总共 0 + 1 + 3 + 3 = 7 次移动。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>seats = [2,2,6,6], students = [1,3,2,6]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>4
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>学生移动方式如下:
|
||||
- 第一位学生从位置 1 移动到位置 2 ,移动 1 次。
|
||||
- 第二位学生从位置 3 移动到位置 6 ,移动 3 次。
|
||||
- 第三位学生不移动。
|
||||
- 第四位学生不移动。
|
||||
总共 1 + 3 + 0 + 0 = 4 次移动。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>n == seats.length == students.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= seats[i], students[j] <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
<p>有一个特殊打字机,它由一个 <strong>圆盘</strong> 和一个 <strong>指针</strong> 组成, 圆盘上标有小写英文字母 <code>'a'</code> 到 <code>'z'</code>。<strong>只有</strong> 当指针指向某个字母时,它才能被键入。指针 <strong>初始时</strong> 指向字符 <code>'a'</code> 。</p>
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/07/31/chart.jpg" style="width: 530px; height: 410px;" />
|
||||
<p>每一秒钟,你可以执行以下操作之一:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>将指针 <strong>顺时针</strong> 或者 <b>逆时针</b> 移动一个字符。</li>
|
||||
<li>键入指针 <strong>当前</strong> 指向的字符。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给你一个字符串 <code>word</code> ,请你返回键入 <code>word</code> 所表示单词的 <b>最少</b> 秒数 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<b>输入:</b>word = "abc"
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>5
|
||||
<strong>解释:
|
||||
</strong>单词按如下操作键入:
|
||||
- 花 1 秒键入字符 'a' in 1 ,因为指针初始指向 'a' ,故不需移动指针。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒将指针顺时针移到 'b' 。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒键入字符 'b' 。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒将指针顺时针移到 'c' 。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒键入字符 'c' 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<b>输入:</b>word = "bza"
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>7
|
||||
<strong>解释:
|
||||
</strong>单词按如下操作键入:
|
||||
- 花 1 秒将指针顺时针移到 'b' 。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒键入字符 'b' 。
|
||||
- 花 2 秒将指针逆时针移到 'z' 。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒键入字符 'z' 。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒将指针顺时针移到 'a' 。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒键入字符 'a' 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<b>输入:</b>word = "zjpc"
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>34
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
单词按如下操作键入:
|
||||
- 花 1 秒将指针逆时针移到 'z' 。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒键入字符 'z' 。
|
||||
- 花 10 秒将指针顺时针移到 'j' 。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒键入字符 'j' 。
|
||||
- 花 6 秒将指针顺时针移到 'p' 。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒键入字符 'p' 。
|
||||
- 花 13 秒将指针逆时针移到 'c' 。
|
||||
- 花 1 秒键入字符 'c' 。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= word.length <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>word</code> 只包含小写英文字母。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
38
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/值和下标之差都在给定的范围内 [7WqeDu].html
Normal file
38
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/值和下标之差都在给定的范围内 [7WqeDu].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个整数数组 <code>nums</code> 和两个整数 <code>k</code> 和 <code>t</code> 。请你判断是否存在 <b>两个不同下标</b> <code>i</code> 和 <code>j</code>,使得 <code>abs(nums[i] - nums[j]) <= t</code> ,同时又满足 <code>abs(i - j) <= k</code><em> </em>。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>如果存在则返回 <code>true</code>,不存在返回 <code>false</code>。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>nums = [1,2,3,1], k<em> </em>= 3, t = 0
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>true</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>nums = [1,0,1,1], k<em> </em>=<em> </em>1, t = 2
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>true</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>nums = [1,5,9,1,5,9], k = 2, t = 3
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>false</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= nums.length <= 2 * 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>-2<sup>31</sup> <= nums[i] <= 2<sup>31</sup> - 1</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= k <= 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= t <= 2<sup>31</sup> - 1</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 220 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/contains-duplicate-iii/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/contains-duplicate-iii/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 <code>nums</code> ,返回 <code>nums</code> 中满足<em> </em><code>i mod 10 == nums[i]</code><em> </em>的最小下标 <code>i</code> ;如果不存在这样的下标,返回<em> </em><code>-1</code><em> </em>。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code>x mod y</code> 表示 <code>x</code> 除以 <code>y</code> 的 <strong>余数</strong> 。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>nums = [0,1,2]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>0
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
i=0: 0 mod 10 = 0 == nums[0].
|
||||
i=1: 1 mod 10 = 1 == nums[1].
|
||||
i=2: 2 mod 10 = 2 == nums[2].
|
||||
所有下标都满足 i mod 10 == nums[i] ,所以返回最小下标 0
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>nums = [4,3,2,1]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>2
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>
|
||||
i=0: 0 mod 10 = 0 != nums[0].
|
||||
i=1: 1 mod 10 = 1 != nums[1].
|
||||
i=2: 2 mod 10 = 2 == nums[2].
|
||||
i=3: 3 mod 10 = 3 != nums[3].
|
||||
2 唯一一个满足 i mod 10 == nums[i] 的下标
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>-1
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>不存在满足 i mod 10 == nums[i] 的下标
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 4:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>nums = [2,1,3,5,2]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>1
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>1 是唯一一个满足 i mod 10 == nums[i] 的下标
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums.length <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>0 <= nums[i] <= 9</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
56
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/允许重复选择元素的组合 [Ygoe9J].html
Normal file
56
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/允许重复选择元素的组合 [Ygoe9J].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个<strong>无重复元素</strong>的正整数数组 <code>candidates</code> 和一个正整数 <code>target</code> ,找出 <code>candidates</code> 中所有可以使数字和为目标数 <code>target</code> 的唯一组合。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><code>candidates</code> 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。如果至少一个所选数字数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。 </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>对于给定的输入,保证和为 <code>target</code> 的唯一组合数少于 <code>150</code> 个。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>candidates = <code>[2,3,6,7], </code>target = <code>7</code>
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[[7],[2,2,3]]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>candidates = [2,3,5]<code>, </code>target = 8
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>candidates = <code>[2], </code>target = <span style="white-space: pre-wrap;">1</span>
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 4:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>candidates = <code>[1], </code>target = <code>1</code>
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[[1]]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 5:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>candidates = <code>[1], </code>target = <code>2</code>
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[[1,1]]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= candidates.length <= 30</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= candidates[i] <= 200</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>candidate</code> 中的每个元素都是独一无二的。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= target <= 500</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 39 题相同: <a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<p>给你一个整数数组 <code>nums</code> ,统计并返回在 <code>nums</code> 中同时至少具有一个严格较小元素和一个严格较大元素的元素数目。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>nums = [11,7,2,15]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>2
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>元素 7 :严格较小元素是元素 2 ,严格较大元素是元素 11 。
|
||||
元素 11 :严格较小元素是元素 7 ,严格较大元素是元素 15 。
|
||||
总计有 2 个元素都满足在 nums 中同时存在一个严格较小元素和一个严格较大元素。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入:</strong>nums = [-3,3,3,90]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>2
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>元素 3 :严格较小元素是元素 -3 ,严格较大元素是元素 90 。
|
||||
由于有两个元素的值为 3 ,总计有 2 个元素都满足在 nums 中同时存在一个严格较小元素和一个严格较大元素。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums.length <= 100</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>-10<sup>5</sup> <= nums[i] <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
<p>你有 <code>n</code> 枚花的种子。每枚种子必须先种下,才能开始生长、开花。播种需要时间,种子的生长也是如此。给你两个下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的整数数组 <code>plantTime</code> 和 <code>growTime</code> ,每个数组的长度都是 <code>n</code> :</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>plantTime[i]</code> 是 <strong>播种</strong> 第 <code>i</code> 枚种子所需的 <strong>完整天数</strong> 。每天,你只能为播种某一枚种子而劳作。<strong>无须</strong> 连续几天都在种同一枚种子,但是种子播种必须在你工作的天数达到 <code>plantTime[i]</code> 之后才算完成。</li>
|
||||
<li><code>growTime[i]</code> 是第 <code>i</code> 枚种子完全种下后生长所需的 <strong>完整天数 </strong>。在它生长的最后一天 <strong>之后</strong> ,将会开花并且永远 <strong>绽放</strong> 。</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>从第 <code>0</code> 开始,你可以按 <strong>任意</strong> 顺序播种种子。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>返回所有种子都开花的 <strong>最早</strong> 一天是第几天。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/12/21/1.png" style="width: 453px; height: 149px;">
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>plantTime = [1,4,3], growTime = [2,3,1]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>9
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>灰色的花盆表示播种的日子,彩色的花盆表示生长的日子,花朵表示开花的日子。
|
||||
一种最优方案是:
|
||||
第 0 天,播种第 0 枚种子,种子生长 2 整天。并在第 3 天开花。
|
||||
第 1、2、3、4 天,播种第 1 枚种子。种子生长 3 整天,并在第 8 天开花。
|
||||
第 5、6、7 天,播种第 2 枚种子。种子生长 1 整天,并在第 9 天开花。
|
||||
因此,在第 9 天,所有种子都开花。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
<img alt="" src="https://assets.leetcode.com/uploads/2021/12/21/2.png" style="width: 454px; height: 184px;">
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>plantTime = [1,2,3,2], growTime = [2,1,2,1]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>9
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>灰色的花盆表示播种的日子,彩色的花盆表示生长的日子,花朵表示开花的日子。
|
||||
一种最优方案是:
|
||||
第 1 天,播种第 0 枚种子,种子生长 2 整天。并在第 4 天开花。
|
||||
第 0、3 天,播种第 1 枚种子。种子生长 1 整天,并在第 5 天开花。
|
||||
第 2、4、5 天,播种第 2 枚种子。种子生长 2 整天,并在第 8 天开花。
|
||||
第 6、7 天,播种第 3 枚种子。种子生长 1 整天,并在第 9 天开花。
|
||||
因此,在第 9 天,所有种子都开花。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong>plantTime = [1], growTime = [1]
|
||||
<strong>输出:</strong>2
|
||||
<strong>解释:</strong>第 0 天,播种第 0 枚种子。种子需要生长 1 整天,然后在第 2 天开花。
|
||||
因此,在第 2 天,所有种子都开花。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>n == plantTime.length == growTime.length</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= plantTime[i], growTime[i] <= 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
21
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/八皇后 [eight-queens-lcci].html
Normal file
21
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/八皇后 [eight-queens-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
<p>设计一种算法,打印 N 皇后在 N × N 棋盘上的各种摆法,其中每个皇后都不同行、不同列,也不在对角线上。这里的“对角线”指的是所有的对角线,不只是平分整个棋盘的那两条对角线。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>注意:</strong>本题相对原题做了扩展</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong> 输入</strong>:4
|
||||
<strong> 输出</strong>:[[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
|
||||
<strong> 解释</strong>: 4 皇后问题存在如下两个不同的解法。
|
||||
[
|
||||
[".Q..", // 解法 1
|
||||
"...Q",
|
||||
"Q...",
|
||||
"..Q."],
|
||||
|
||||
["..Q.", // 解法 2
|
||||
"Q...",
|
||||
"...Q",
|
||||
".Q.."]
|
||||
]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
41
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/兰顿蚂蚁 [langtons-ant-lcci].html
Normal file
41
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/兰顿蚂蚁 [langtons-ant-lcci].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
<p>一只蚂蚁坐在由白色和黑色方格构成的无限网格上。开始时,网格全白,蚂蚁面向右侧。每行走一步,蚂蚁执行以下操作。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>(1) 如果在白色方格上,则翻转方格的颜色,向右(顺时针)转 90 度,并向前移动一个单位。<br>
|
||||
(2) 如果在黑色方格上,则翻转方格的颜色,向左(逆时针方向)转 90 度,并向前移动一个单位。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>编写程序来模拟蚂蚁执行的前 K 个动作,并返回最终的网格。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>网格由数组表示,每个元素是一个字符串,代表网格中的一行,黑色方格由 <code>'X'</code> 表示,白色方格由 <code>'_'</code> 表示,蚂蚁所在的位置由 <code>'L'</code>, <code>'U'</code>, <code>'R'</code>, <code>'D'</code> 表示,分别表示蚂蚁 左、上、右、下 的朝向。只需要返回能够包含蚂蚁走过的所有方格的最小矩形。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> 0
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>["R"]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> 2
|
||||
<strong>输出:
|
||||
</strong>[
|
||||
"_X",
|
||||
"LX"
|
||||
]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>输入:</strong> 5
|
||||
<strong>输出:
|
||||
</strong>[
|
||||
"_U",
|
||||
"X_",
|
||||
"XX"
|
||||
]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>说明:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>K <= 100000</code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
34
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/出现频率最高的 k 个数字 [g5c51o].html
Normal file
34
算法题(国内版)/problem (Chinese)/出现频率最高的 k 个数字 [g5c51o].html
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<p>给定一个整数数组 <code>nums</code> 和一个整数 <code>k</code> ,请返回其中出现频率前 <code>k</code> 高的元素。可以按 <strong>任意顺序</strong> 返回答案。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[1,2]
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
<strong>输入: </strong>nums = [1], k = 1
|
||||
<strong>输出: </strong>[1]</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= nums.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>k</code> 的取值范围是 <code>[1, 数组中不相同的元素的个数]</code></li>
|
||||
<li>题目数据保证答案唯一,换句话说,数组中前 <code>k</code> 个高频元素的集合是唯一的</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>进阶:</strong>所设计算法的时间复杂度 <strong>必须</strong> 优于 <code>O(n log n)</code> ,其中 <code>n</code><em> </em>是数组大小。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><meta charset="UTF-8" />注意:本题与主站 347 题相同:<a href="https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/">https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/top-k-frequent-elements/</a></p>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
<p>你驾驶出租车行驶在一条有 <code>n</code> 个地点的路上。这 <code>n</code> 个地点从近到远编号为 <code>1</code> 到 <code>n</code> ,你想要从 <code>1</code> 开到 <code>n</code> ,通过接乘客订单盈利。你只能沿着编号递增的方向前进,不能改变方向。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>乘客信息用一个下标从 <strong>0</strong> 开始的二维数组 <code>rides</code> 表示,其中 <code>rides[i] = [start<sub>i</sub>, end<sub>i</sub>, tip<sub>i</sub>]</code> 表示第 <code>i</code> 位乘客需要从地点 <code>start<sub>i</sub></code> 前往 <code>end<sub>i</sub></code> ,愿意支付 <code>tip<sub>i</sub></code> 元的小费。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>每一位</strong> 你选择接单的乘客 <code>i</code> ,你可以 <strong>盈利</strong> <code>end<sub>i</sub> - start<sub>i</sub> + tip<sub>i</sub></code> 元。你同时 <strong>最多</strong> 只能接一个订单。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>给你 <code>n</code> 和 <code>rides</code> ,请你返回在最优接单方案下,你能盈利 <strong>最多</strong> 多少元。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>注意:</strong>你可以在一个地点放下一位乘客,并在同一个地点接上另一位乘客。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>n = 5, rides = [<em><strong>[2,5,4]</strong></em>,[1,5,1]]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>7
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>我们可以接乘客 0 的订单,获得 5 - 2 + 4 = 7 元。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><b>输入:</b>n = 20, rides = [[1,6,1],<strong><em>[3,10,2]</em></strong>,<em><strong>[10,12,3]</strong></em>,[11,12,2],[12,15,2],<strong><em>[13,18,1]</em></strong>]
|
||||
<b>输出:</b>20
|
||||
<b>解释:</b>我们可以接以下乘客的订单:
|
||||
- 将乘客 1 从地点 3 送往地点 10 ,获得 10 - 3 + 2 = 9 元。
|
||||
- 将乘客 2 从地点 10 送往地点 12 ,获得 12 - 10 + 3 = 5 元。
|
||||
- 将乘客 5 从地点 13 送往地点 18 ,获得 18 - 13 + 1 = 6 元。
|
||||
我们总共获得 9 + 5 + 6 = 20 元。</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
<p> </p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p><strong>提示:</strong></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= rides.length <= 3 * 10<sup>4</sup></code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>rides[i].length == 3</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= start<sub>i</sub> < end<sub>i</sub> <= n</code></li>
|
||||
<li><code>1 <= tip<sub>i</sub> <= 10<sup>5</sup></code></li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user